Credit: New Jersey Institute of Technology
NJIT researchers are finding alternative solutions to a material that has become an essential, yet costly, building block in the supply chain of today's smart device-driven world—cobalt.
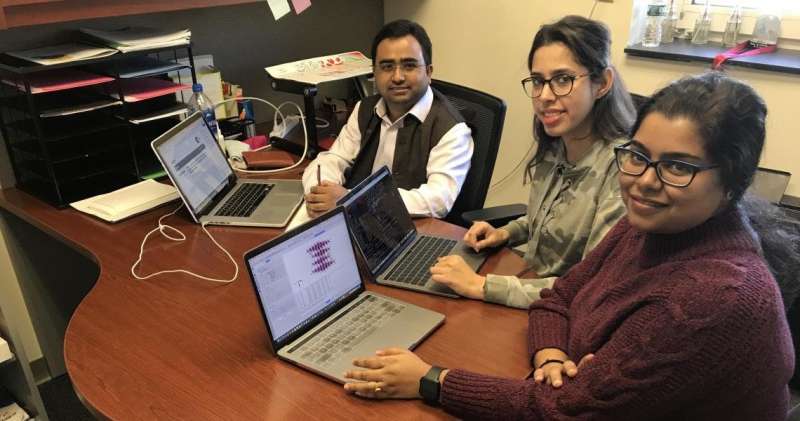
Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering Dibakar Datta and his research team were recently published in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, a prestigious journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Professor Datta's team, alongside collaborators from three other universities, have computationally designed electrode materials and procedures that reduce the cobalt concentrations in ubiquitous rechargeable batteries.
Cobalt is a very expensive and toxic chemical element and can pose serious health risks to those exposed to it. Recently, a CBS News investigation showed the hazardous conditions for cobalt mining.
In the research team's work, they showed that batteries can be designed with a lower cobalt concentration and still have effective capacity and charge measurements. Creating batteries with low or no cobalt concentrations will create a more environmentally friendly and safer alternative by decreasing the demand of the toxic element.
Credit: CBS
More information: Kamalika Ghatak et al. Effect of cobalt content on the electrochemical properties and structural stability of NCA type cathode materials, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (2018). DOI: 10.1039/C8CP03237H
Journal information: Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
Provided by New Jersey Institute of Technology