PGDx machine learning approach outperforms existing mutation detection methods in study
Personal Genome Diagnostics today announced that its machine learning-based technology, CerebroTM, outperforms existing methods to identify tumor-specific or somatic mutations, enabling more accurate NGS clinical test results. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, was conducted using analysis of data from 1,368 samples.
"Increasingly, NGS diagnostic tests are being used to identify genetic alterations that help oncologists make decisions with their patients about the potential effectiveness of therapies. However, different NGS approaches have varying results, calling into question the ability of NGS to detect real mutations," said Sam Angiuoli, Ph.D., chief information officer at PGDx. "We know it is absolutely critical to get the right answer for patients, so we pioneered the development of automated NGS software that incorporates machine learning strategies to improve the accuracy of somatic mutation detection. As this study reveals, our approach yields better results compared to alternatives and highlights the importance of combining state-of-the-art software and data science in genomic testing."
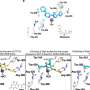
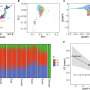
Cerebro's machine learning approach analyzes a wide variety of characteristics to assess whether any given identified mutation is real. The accuracy of the Cerebro technology was compared to existing methods for somatic mutation identification using simulated and experimentally validated whole-exome and targeted gene analyses of cancer specimens. Cerebro was able to detect tumor alterations with higher sensitivity and positive predictive value (PPV) compared against other methods.
The Cerebro study also evaluated the importance of improved somatic mutation detection in clinical NGS assays. PGDx performed head-to-head comparisons of clinical sequencing with or without the Cerebro machine learning approach, including a comparison of predicted outcomes for patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade.
"Highly accurate mutation detection may be particularly important for biomarkers like tumor mutation burden, or TMB, which correlates with response to immunotherapies. Our data showed improved classification of patients when using Cerebro and highlights the importance of accurate mutation detection on treatment decisions," said Dr. Angiuoli.
This study brings to light the variability in detecting tumor-specific alterations across different NGS tests, underscores the importance of standardization as NGS tests move into more routine clinical use, and demonstrates the higher accuracy of PGDx's solution when compared against commercially available methods from other diagnostic companies.
"Developing a highly-accurate bioinformatics software solution that automates mutation detection is integral to PGDx's approach to create a complete solution, from DNA sample to high-quality patient result," noted John Simmons, Ph.D., Director of Translational Science and Diagnostics at PGDx. "Our decentralized product approach includes optimized assay chemistry combined with a fully automated bioinformatics software platform, which reduces subjective analyses and increases reproducible results. This comprehensive solution will enable local testing in molecular laboratories worldwide, with a faster turnaround of reliable results to support critical clinical decisions."
More information: D.E. Wood el al., "A machine learning approach for somatic mutation discovery," Science Translational Medicine (2018). stm.sciencemag.org/lookup/doi/ … scitranslmed.aar7939