November 21, 2018 feature
RoboTurk: A crowdsourcing platform for imitation learning in robotics
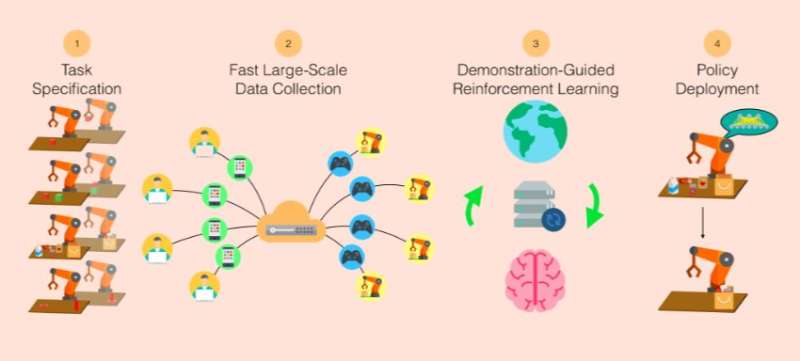
Imitation learning is a branch of machine learning that trains machines to mimic human behavior while completing particular tasks. These techniques show great promise in the field of robotics, as they tackle some of the shortcomings of reinforcement learning, such as exploration and reward specification.
Despite encouraging results, imitation learning studies have so far been limited to modest-sized datasets due to difficulties in collecting large quantities of task demonstrations using existing methods. To address these limitations, a team of researchers supervised by Dr. Silvio Savarese and Dr. Fei-Fei Li at Stanford University have developed RoboTurk, a crowdsourcing platform for high-quality 6-DoF trajectory-based teleoperation using widely available smartphone devices.
"We wanted to create something like ImageNet for Robotics," Ajay Mandlekar, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. "We believe that data is a key limitation in the field of robot learning. While there are plenty of methods that learn from data, such as data-driven control and reinforcement learning, most methods collect their own data. As a result, the data is often of a low quality, for instance resulting in the robot moving its arm randomly. This type of exploration can be difficult and unsafe, but we believe that humans can help."
ImageNet is a renowned image database created by Dr. Li, commonly used in computer vision and object recognition research. The crowdsourcing platform developed by Stanford Vision and Learning Lab was designed to serve as a similar resource for robotics and imitation learning studies.
"Unlike ImageNet, such a data collection system needed to be dynamic, allowing us to collect data repeatedly, often on-demand, and perhaps even using collaborative learning," Yuke Zhu, who was also involved in the development of Roboturk, told TechXplore. "This is because the data that is collected depends on what types of actions the robot takes in the environment."
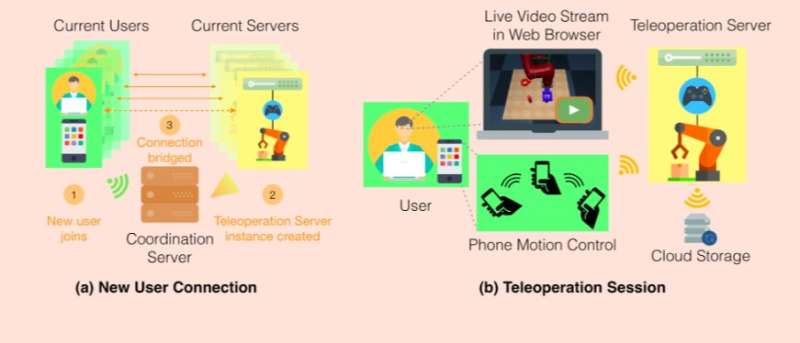
The researchers' ultimate goal is to train robots on advanced manipulation skills, allowing them to complete tasks within industrial settings such as packaging or assembly. They found that while imitation learning showed great potential in this context, existing datasets were very limited due to difficulties in collecting large quantities of task demonstrations.
"In other domains such as computer vision and natural language processing, large-scale supervision for datasets is often collected with the assistance of crowdsourcing," Mandlekar said. "This enables a scalable mechanism for diverse human supervision on an extensive set of problem instances. However, collecting large amounts of data has been a challenge for robotics tasks, as they demand real-time interaction and feedback from annotators, placing difficult constraints on remote teleoperation platforms."
The group at Stanford Vision and Learning Lab hence developed RoboTurk, a crowdsourcing platform that allows researchers to scale up the skills and tasks that robots can perform autonomously, through the use of scalable human supervision. Via RoboTurk, remote workers can log onto a website and collect task demonstrations, using their smartphone as a motion controller.
"RoboTurk is supported by a cloud-based simulation backend that streams video to a client's web browser using low-latency communication protocols," Mandlekar explained. "This ensures homogenous quality of service regardless of a client's computer resources, resulting in a platform that is intuitive to use and has a low barrier to entry, which are the core requirements of a crowdsourced task. RoboTurk supports multiple robots, tasks, and simulators, and can easily be extended to support others."
The researchers evaluated their platform on three manipulation tasks of varying durations, ranging from 15 to 120 seconds. They found that RoboTurk shared statistical similarities with special purpose hardware, such as virtual reality controllers. They also observed that poor network conditions did not substantially affect users' ability to perform tasks successfully on the platform. Using RoboTurk, they collected 137.5 hours of manipulation data from remote workers, with over 2200 successful task demonstrations in 22 hours of total system usage.
"I think that the most meaningful part of the platform is how it will enable humans and robots to interact," Animesh Garg, postdoctoral student leading the project, told TechXplore. "Robots are the smart tools of the future. We should not think of them as a replacement for humans but rather as a way to extend our capabilities. This empowers humans to be more productive and focus on higher-level intelligence problems, in the same way in which the advent of computers made it easier for people to use math as a tool to solve problems of interest."
RoboTurk effectively enables policy learning on multi-step manipulation tasks with sparse rewards. In addition, Mandlekar and his colleagues found that using larger quantities of demonstrations during policy learning had notable benefits, leading to better performance and greater learning consistency.
In the future, RoboTurk could become a key resource in the field of robotics, aiding the development of more advanced and better performing robots. The researchers are now applying RoboTurk to real robots, while also developing algorithms that can use the data they collected to teach robots low-level skills.
"Robots are a very exciting technology that will enable people to be more productive and independent in all spheres of human activity, for instance providing a helping hand in the kitchen, caretakers for the senior population, and better care for patients," Garg said. "One of the things that excites us is the democratization of manufacturing. This technology could enable people to make and sell custom products without the need of special purpose equipment, just as YouTube has democratized content creation and distribution, allowing anyone to create and share videos."
More information: RoboTurk: A crowdsourcing platform for robotic skill learning through imitation. arXiv: 1811.02790 [cs.RO]. arxiv.org/abs/1811.02790
© 2018 Science X Network