Semiconductor material analysis made possible with artificial intelligence
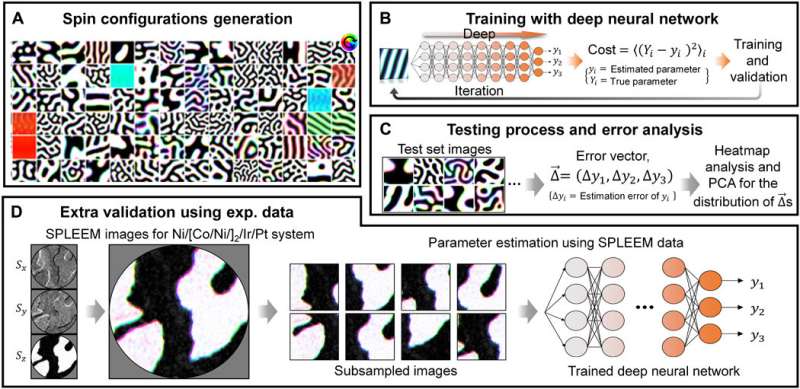
Studies on spintronics, which deal with the intrinsic spin of electrons and the field of electronic engineering, are actively conducted to address the limitations of the integration level of silicon semiconductors currently in use and to develop ultra-low-power and high-performance next-generation semiconductors. Magnetic materials are one of the most commonly used materials to develop spintronics devices such as magneto-resistive random-access memory (MRAM). Therefore, it is essential to accurately identify properties of the magnetic materials, such as thermal stability, dynamic behaviors and the ground state configuration, through the analysis of the magnetic Hamiltonian and its parameters.
Previously, the magnetic Hamiltonian parameters were directly measured through various experiments in order to acquire more accurate and deeper understanding of the properties of magnetic materials, and such processes required extensive amount of time and resources.
To overcome these limitations, researchers in South Korea have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that can analyze magnetic systems in an instant. The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) reported that the collaborative research team led by Dr. Heeyong Kwon and Dr. Junwoo Choi from Spin Convergence Research Center and Professor Changyeon Won from Kyung Hee University developed a technique for estimating magnetic Hamiltonian parameters from spin structure images using AI techniques.
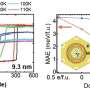
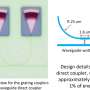
They constructed a deep neural network and trained it with machine-learning algorithms and existing magnetic domain images. As a result, the magnetic Hamiltonian parameters could be estimated in real time by inputting spin structure images obtained from electron microscope. Further, when compared with the experimentally investigated parameter values, the estimation errors of the AI system were less than 1%, indicating high estimation accuracy. According to the team, the developed AI system is capable of completing material parameter estimation process that previously took up to tens of hours in an instant by using deep-learning techniques.
"We presented a novel approach on how AI technologies can be implemented to analyze the properties of magnetic systems," Dr. Hee-young Kwon at KIST said. "We expect that new methods for studying physical systems using such AI technologies will be able to reduce the gap between experimental and theoretical aspects, and will further lead to expanding a new research field of convergence of AI technology and fundamental science research."
More information: H. Y. Kwon et al, Magnetic Hamiltonian parameter estimation using deep learning techniques, Science Advances (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb0872