New energy systems could cause a sea change in energy efficiency during shipping
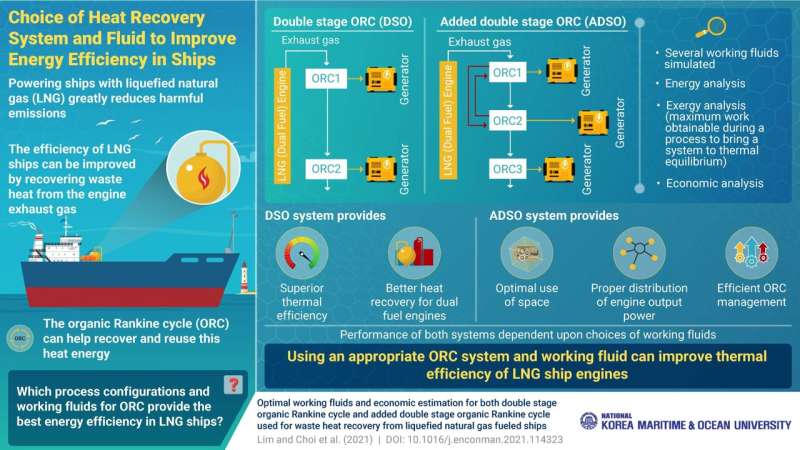
Using liquefied natural gas (LNG) as fuel can help ships reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. But LNG ships are currently inefficient, with massive heat losses. Thankfully, researchers have developed novel heat recovery systems that can provide superior energy efficiency, leading to better environmental outcomes.
The desire to limit greenhouse gas emissions has increased interest in liquefied natural gas (LNG) ships, which produces considerably less emissions than those running on other fossil fuels. But LNG is expensive, making the maximization of LNG engine energy efficiencies paramount to their widespread use.
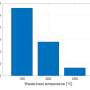
At present, LNG ships lose up to 25% of their input heat in the form of exhaust gas. Recovering this heat is key to energy efficiency. In a recent study published in Energy Conversion and Management, a team from Korea Maritime & Ocean University, led by Dr. Yeong-Seok Choi, developed two novel heat recovery systems that can boost energy efficiency in LNG ships. Dr. Choi explains, "by increasing the energy efficiency of LNG systems, we are directly contributing to environmental protection."
The research is based on what is called the 'organic Rankine cycle (ORC).' In ORC, an organic fluid is first boiled, then used to turn a turbine to generate electricity, during which it loses heat. The fluid is then condensed and reheated in a continuation of the cycle. In LNG ships, ORC also allows the preheating of cold fuel (LNG is stored at -160°C) before burning.
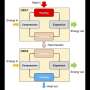
The research team developed two heat recovery systems. The first, the double stage ORC system (DSO), uses the heat from the engine exhaust gas to run two ORCs with connections to two generators. The second, the added double stage ORC system (ADSO), additionally features a third ORC; also, two of its ORCs exchange heat with each other.
The team examined the workings of DSO and ADSO with combinations of different organic fluids. They then performed energy, exergy (maximum work derived from a heat exchange process), and economic analyses on the systems.
They found that while DSO had better overall energy efficiency, ADSO was more suitable for cramped engine spaces. They also saw that performance depended greatly on fluid combination. Overall, the new designs achieved substantial improvements in energy efficiency.
"Although our research is focused on shipping, this work can be applied to several other industries and cryogenic hydrogen research as well," says Dr. Choi.
With such innovative designs, energy efficient engine systems could soon become an industrial reality for ships.
More information: Tae-Woo Lim et al, Optimal working fluids and economic estimation for both double stage organic Rankine cycle and added double stage organic Rankine cycle used for waste heat recovery from liquefied natural gas fueled ships, Energy Conversion and Management (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114323