Credit: Seidu et al., APL Mater. 9, 111102 (2021)
Energy is an essential commodity of our existence, as such, having a sustainable, renewable and affordable energy source is vital. Of all the renewable energy sources, the sun is the most promising due to the vast amount of energy it radiates to the earth surface. To benefit from this vast energy from the sun, a comprehensive study into photovoltaics is needed. In this article, we present our findings from the surface study of a perovskite material, methyl ammonium triiodide (MAPbI3).
The results of a new theoretical study into the surfaces of methyl ammonium triiodide (MAPbI3), the most studied perovskite material with potential for photovoltaic applications, highlights both the complexity of such surfaces and paves the way for future surface science and interface studies.
MAPbI3 is an organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite material which has remarkable electronic properties, capable of becoming the most efficient third generation optoelectronic material.
These properties make it particularly suitable for use in photovoltaic applications.
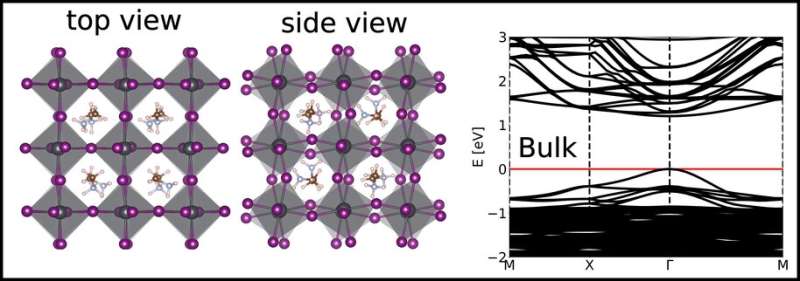
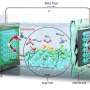
A recent article authored by Azimatu Seidu unravels the (001) surface of MAPbI3 using theoretical methods. In particular, Seidu and co-workers investigated the atomic and electronic structure of the tetragonal (I4cm) phase of MAPbI3 surface. For this phase, Seidu studied surfaces with MAI- (MAI-T) and PbI>2-terminations (PbI2-T) and found MAI-T to be more stable than PbI2-T.
In addition, the work explored surface reconstructions of MAI-T by adding and removing constituent elements (MeNH2, MA, Pb, and I) as well as their complexes (MAI, HI and PbI2). Interestingly, they found out that adding or removing nonpolar MAI and PbI2 units, turned out to be most stable.
These results and previous findings from Seidu and co-workers now offer concrete guidance for growing favorable perovskite surfaces for use in photovoltaics. Seidu now plans to combine her recent work and previous search on suitable coating materials for perovskites to model stable and robust perovskites for solar applications. The future research and the final part of Seidu's Ph.D. combines a machine learning based Bayesian optimization structural search (BOSS) and density functional theory (DFT) to obtain stable coating-perovskite interfaces.
More information: Azimatu Seidu et al, Surface reconstruction of tetragonal methylammonium lead triiodide, APL Materials (2021). DOI: 10.1063/5.0067108
Provided by Aalto University