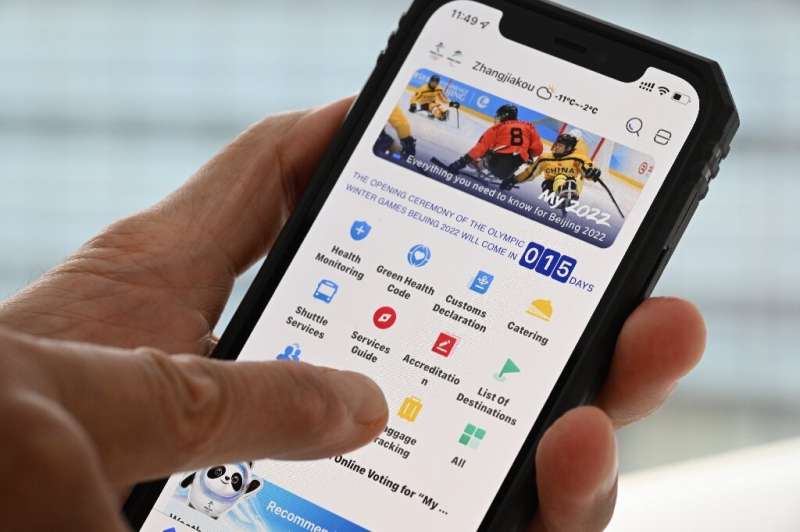
People taking part in the Games have to download a health-tracking app called MY2022.
An app that Winter Olympics attendees must use has been patched, a Chinese official told AFP Thursday, after cyber security researchers said they had found a "simple but devastating" flaw that could allow data leaks.
Next month's Games are being held in a bubble that separates participants from the rest of the population as part of China's strict zero-Covid policy.
Those taking part—from foreign athletes, delegates and media to the army of local volunteers and officials—have to download a health-tracking app called MY2022.
Users report their health status daily through the app which collects data including vaccination status and coronavirus test results, as well as travel and passport details.
Earlier this week researchers at the University of Toronto's Citizen Lab said they discovered the app's security flaws could allow data including health information and voice messages to leak, which could then be read by "eavesdroppers" such as Wi-Fi hotspot operators.
But a senior Chinese Olympic official said any bugs had now been fixed.
"There is definitely no data leakage," Beijing Olympics Organising Committee (BOCOG) tech chief Yu Hong told AFP, adding that the app's user and privacy guidelines were reviewed by the International Olympic Committee.
"The security loopholes have already been fixed. If they existed in earlier versions, they have been fixed in the latest version."
The app's developers have been in email contact with Citizen Lab since Wednesday, Yu added, promising that there will be "relevant discussions" on follow-up work.
Yu did not deny there may have been security flaws in previous versions of the app and she suggested that BOCOG had not been aware of them.
"During development we have continued to test and use it. When new usage conditions appear some new technological imperfections may be discovered, these can be called loopholes," she said.
Data laws
Citizen Lab earlier said it had notified organisers about the issues in early December but received no reply.
However, Yu said organisers never saw the request because it was sent to an old email address.
China's data security laws require that health and medical data be encrypted during transmission and storage.
The Citizen Lab report claimed that the app's inadequate encryption could violate Chinese law, as well as Google and Apple mobile software policies.
"China has a history of undermining encryption technology to perform political censorship and surveillance," researcher Jeffrey Knockel wrote in the report.
Researchers also discovered the app's Android code contained an apparently inactive blacklist of over 2,400 "politically sensitive" phrases, and that it had a separate function to report other users' speech for "politically sensitive content".
But organisers denied ever requesting these functions, and said they have asked the developer to look into it.
They added that app health data would primarily be shared with virus control authorities, after the report claimed this was unclear.
"Use of data by individuals and departments is only permitted after the IOC confirms it," Yu said.
China maintains the world's most sophisticated digital tools to monitor and censor the internet for its citizens, blocking major Western platforms such as Twitter, Facebook and YouTube.
In recent days, Olympic associations in multiple Western countries have warned athletes to leave personal devices at home and bring "burner" phones to China.
Analysts have also warned of cybersecurity risks such as data theft and surveillance targeting attendees using public Wi-Fi networks and official SIM cards provided by organisers.
However, organisers and the Chinese government have dismissed such concerns as unfounded.
"The government will not monitor individuals' phones in any form," Yu said.
The app also provides a range of daily living services for users, such as translation, weather, transport schedules and accommodation booking.
© 2022 AFP