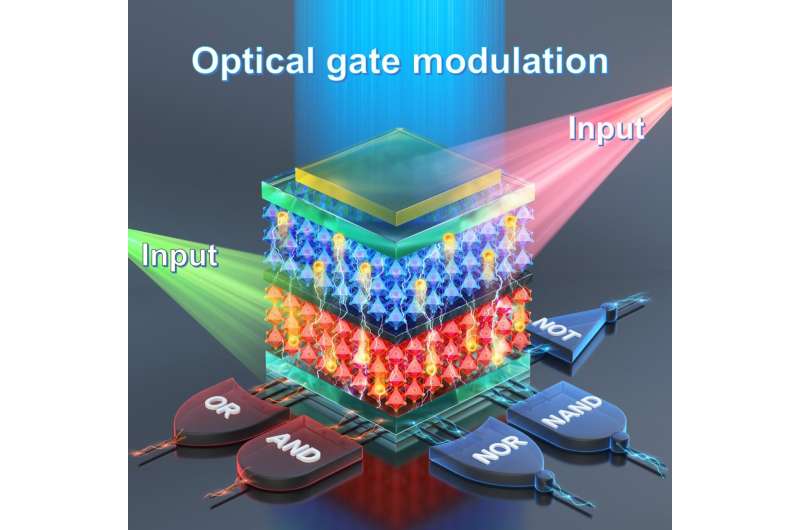
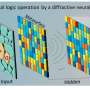
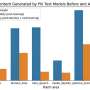
Three-dimensional bar charts for all the outputs (“OR”, “AND”, “NAND”, “NOR”, and “NOT”) obtained from the 64 pixels. The red and blue bars show clear bipolar spectral photoresponses of all the pixels with reference to the fiducial level of 0 nA (gray face). Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Demand is increasing for computers that can quickly calculate and process large amounts of information, as artificial intelligence, self-driving cars, drones, and metaverse technologies are drawing attention as core industries of the future. However, electronic semiconductor logic gates, which serve as the brains of computers today, have limited capacity in high-speed data calculation and processing, and have disadvantages in that they consume a lot of energy and generate considerable heat.
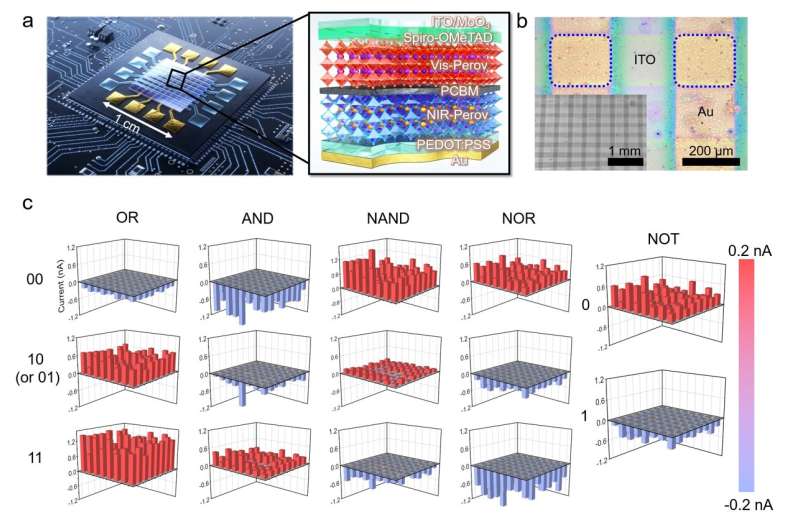
Research teams at KIST and Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, led by Dr. Yusin Pak at the Sensor System Research Center (KIST) and Professor Gun Young Jung at the School of Materials Science and Engineering (GIST), have developed ultra-high-speed, high-efficiency optoelectronic logic gates (OELGs) by using organic-inorganic perovskite photodiodes.
The optoelectronic logic gate has high-speed and high-efficiency characteristics; it uses light as an input signal, and demonstrates low energy loss physically, and can operate without electrical power supply using only light energy. The research teams implemented a stacked perovskite optoelectronic logic gate. Two layers of perovskite thin films are vertically stacked like a sandwich and proved that the desired binary logic operation is possible by inputting two lights of different wavelengths and intensities.
As the perovskite optoelectronic logic gate can freely change the photocurrent polarity using light, executing more than one logic gate operation result for the same input value is possible. Therefore, compared to the existing logic gate that can only perform one logical operation on one device, the newly developed one can implement all five different basic logic operations such as AND, OR, NAND, NOR, and NOT. It enables the development of optical processors with high spatial efficiency and integration, as one logic gate can function like five logic gates.
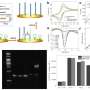
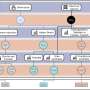
Conceptual image of an optical processor chip for optical computers using perovskite optoelectronic logic Gates. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Dr. Pak (KIST) said, "Perovskite optoelectronic logic gates that execute multiple logic operations in response to optical input are expected to be used for ultra-small and low-power universal optical sensor platforms in the future." Prof. Jung (GIST) said, "The optoelectronic logic gate developed through this research is an outcome of optical computing R&D that realizes five basic logic operations into one device, and will greatly contribute to next-generation optical communication, optical network, and healthcare R&D."
The study is published in Nature Communications.
More information: Woochul Kim et al, Perovskite multifunctional logic gates via bipolar photoresponse of single photodetector, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28374-w
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by National Research Council of Science & Technology