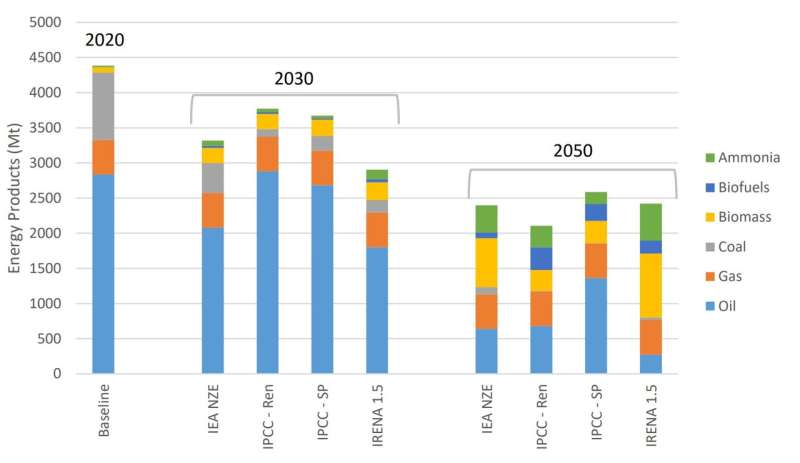
Potential seaborne trade outcomes for the 1.5˚C scenarios, assuming higher levels of trade of emergent lowcarbon fuels and deployment at scale of carbon capture and storage technologies. Credit: Shipping’s Role in the Global Energy Transition (2022)
New research from the Tyndall Centre at The University of Manchester highlights an urgent global need for investment in green fuels this decade to meet the Paris Climate goals.
A new report published today from the Tyndall Centre at The University of Manchester has highlighted the major role the shipping sector will play in transporting the green fuels necessary to meet global climate goals. But it found a yawning gap between announced government led projects and what is required, calling for the creation of far stronger national policies on low-carbon fuels. The report is being officially discussed at this year's UN climate conference, COP 27.
The report's authors identify growth in low-carbon hydrogen and sustainable bioenergy as essential to meet the Paris Climate Agreement's goals. But they found that a lack of enabling policies from governments, such as guaranteeing markets and prices for producers and consumers, was holding back investment in the shipping infrastructure needed to support the global energy transition.
The world needs 50-150 million tons of low-carbon hydrogen by 2030, but there is a major gap between this and what is planned to date: already-announced projects will only produce 24 million tons by 2030, according to the International Energy Authority. Worryingly, only 4% of these projects have a final investment decision. The Tyndall Centre called for stronger Government policies to give low-carbon hydrogen producers, shippers and consumers the confidence they need to invest.
Report co-author Professor Alice Larkin said, "New green fuels are essential to meet the Paris climate goals, and there is a pivotal role for the shipping sector in transporting them. But production of green fuels must be scaled up—there is a yawning gap between current plans and what is needed to meet the Paris goals."
Credit: University of Manchester
The report identifies a major role for the shipping sector in this global energy transition, transporting bioenergy, and hydrogen converted into ammonia. It found that the sea-transport of ammonia and bioenergy in the coming decades could match shipments of gas and coal today. However, this would require around 20 large new ammonia carriers a year, to link green hydrogen producers with consumers.
Given the 2–3-year timeline for constructing new vessels, shipping industry representatives said they needed certainty on hydrogen production as soon as possible to be able to justify the necessary investments in new infrastructure. The report was commissioned and welcomed by the International Chamber of shipping and called on governments attending COP27 to send "stronger market signals" to the shipping industry to reduce fears that any new ships built to transport low-carbon fuels would never be used.
The Tyndall Centre's report identified several potential considerations for government policy to increase their effectiveness at enabling investment. These include introducing mandates for increasing percentages of green hydrogen, creating 'production credits' for the production of hydrogen, or providing guaranteed markets and prices for producers and consumers. Such measures are already being trialed in the U.S., Germany, and India.
Guy Platten, secretary general of the International Chamber of Shipping said, "The shipping industry knows it has a huge part to play in global decarbonization in the coming decades, transporting the new green fuels the world's economy needs. But for us to invest, governments need far stronger policies to de-risk green hydrogen production."
"National Hydrogen strategies must include an explicit focus on supporting the transport infrastructure needed for both imports and exports. Industry is ready to respond but we urgently need stronger market signals and infrastructure investment to make this a reality."
More information: Report: www.ics-shipping.org/wp-conten … nergy-Transition.pdf
Provided by University of Manchester