Team develops image deep learning technology to present VR and AR screens more vividly and realistically

Professor Jin Kyong-hwan's research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) has developed image processing deep learning technology that reduces memory speed and increases resolution by 3dB compared to existing technologies.
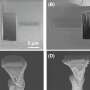
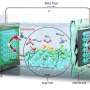
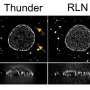
Developed through joint research with Choi Kwang-pyo of Samsung Research, this technology reduces aliasing phenomenon on the screen compared to existing signal processing-based image interpolation technology (Bicubic interpolation), thus producing more natural video output. In particular, it can restore the high-frequency part of images clearly. It is expected to display a natural screen when using VR or AR.
Signal processing-based image interpolation technology (Bicubic interpolation) preserves desired images in various environments by designating a specific location of an image. It has the advantage of saving memory and speed, but deteriorates the quality and deforms the image.
To address this issue, deep learning-based, ultra-high-resolution video image conversion technologies were developed, but most of them are convolutional artificial intelligence network-based technologies, which have the disadvantage of inaccurate estimation of values between pixels, which can lead to image deformation. Implicit expression neural network technology to overcome these disadvantages is drawing attention, but the disadvantage of implicit expression neural network technology is that it cannot capture high-frequency components, and it increases memory and speed.
Professor Jin Kyong-hwan's research team developed a technology that resolves the image into several frequencies so that the characteristics of high-frequency components can be expressed in the image, and reassigns coordinates to resolved frequencies using implicit expression neural network technology so that the image can be shown more clearly.
It can be described as a new technology that combines Fourier analysis, which is an image deep learning technology, and implicit expression neural network technology. The newly implemented technology can improve implicit expression neural networks that could not restore high-frequency components by resolving essential frequency components in restoring images through an artificial intelligence network.
Professor Jin Kyong-hwan said, "The technology developed this time is excellent, as it shows higher restoration performance and consumes less memory than technology used in the existing image warping field. We hope that the technology is utilized for image quality restoration and image editing in the future and hope that it will contribute to both academia and industries."
More information: Jaewon Lee et al, Learning Local Implicit Fourier Representation for Image Warping, arXiv (2022). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2207.01831