This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
preprint
trusted source
proofread
An energy-efficient text-to-audio AI
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems will inspire an explosion of creativity in the music industry and beyond, according to the University of Surrey researchers who are inviting the public to test out their new text-to-audio model.
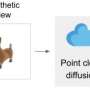
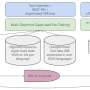
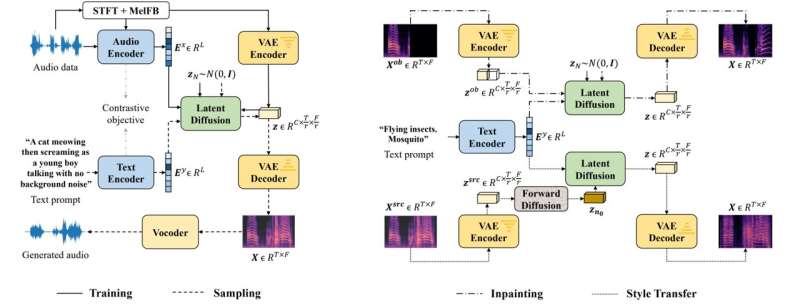
AudioLDM is a new AI-based system from Surrey that allows users to submit a text prompt, which is then used to generate a corresponding audio clip. The system can process prompts and deliver clips using less computational power than current AI systems without compromising sound quality or the users' ability to manipulate clips.
The general public is able to try out AudioLDM by visiting its Hugging Face space. Their code is also open-sourced on GitHub with 1000+ stars.
Such a system could be used by sound designers in a variety of applications, such as film-making, game design, digital art, virtual reality, metaverse, and a digital assistant for the visually impaired.
Haohe Liu, project lead from the University of Surrey, said, "Generative AI has the potential to transform every sector, including music and sound creation."
"With AudioLDM, we show that anyone can create high-quality and unique samples in seconds with very little computing power. While there are some legitimate concerns about the technology, there is no doubt that AI will open doors for many within these creative industries and inspire an explosion of new ideas."
Surrey's open-sourced model is built in a semi-supervised way with a method called Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP). Using the CLAP method, AudioLDM can be trained on massive amounts of diverse audio data without text labeling, significantly improving model capacity.
Wenwu Wang, professor in signal processing and machine learning at the University of Surrey, said, "What makes AudioLDM special is not just that it can create sound clips from text prompts, but that it can create new sounds based on the same text without requiring retraining."
"This saves time and resources since it doesn't require additional training. As generative AI becomes part and parcel of our daily lives, it's important that we start thinking about the energy required to power up the computers that run these technologies. AudioLDM is a step in the right direction."
The user community has created a variety of music clips using AudioLDM in different genres.
AudioLDM is a research demonstrator project and relies on the current UK copyright exception exemption for data mining for non-commercial research. The paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.
More information: Haohe Liu et al, AudioLDM: Text-to-Audio Generation with Latent Diffusion Models, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2301.12503