Decarbonization scenario model analyzes ambitious pathways to net-zero carbon emissions
While the world would love to have a quick fix, there is no one specific pathway to stop or slow the rate of climate change.
51 minutes ago
0
0
Business
While the world would love to have a quick fix, there is no one specific pathway to stop or slow the rate of climate change.
51 minutes ago
0
0
Energy & Green Tech

In a glimmer of progress for the daunting task of reducing air travel's climate impact, a newly built plant in rural Georgia is expected to begin pumping out the world's first commercial quantities of a new type of cleaner ...
Apr 15, 2024
0
8
Energy & Green Tech

It's a major contributor to climate change—the way buildings and roads are made with concrete. It's also a problem that's growing as more of the world develops. So the race has been on to find solutions for a material that's ...
Apr 12, 2024
1
64
Automotive

British luxury carmaker Aston Martin Lagonda will continue to produce traditional combustion-engine vehicles for as long as legally possible, its boss told UK media this week.
Apr 11, 2024
0
4
Engineering
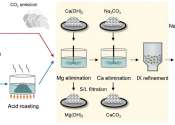
Manufacturers of secondary battery cells (LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and SK) have been insisting on very stringent purity specifications from suppliers of cathode materials to ensure a consistent quality output.
Apr 1, 2024
0
44
Business

Lower-income communities across the United States have long been much slower to adopt solar power than their affluent neighbors, even when local and federal agencies offer tax breaks and other financial incentives.
Mar 28, 2024
0
34
Energy & Green Tech

Japan announced plans on Wednesday to develop a next-generation passenger jet over the next decade after the last struggling attempt, led by a private company, was scrapped a year ago.
Mar 27, 2024
0
43
Engineering

The construction sector today faces several challenges. Natural sand is fast becoming a scarce resource—we might run out of it by 2050. Carbon dioxide emissions, especially from manufacturing cement or fired clay bricks, ...
Mar 27, 2024
0
3
Consumer & Gadgets

The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency released strict new emissions limits on March 20, 2024, for cars built from 2027 through 2032. The final rule for Multi-Pollutant Emissions Standards caps a process that started almost ...
Mar 24, 2024
0
1
Automotive

The chief executive of French automaker Renault called Tuesday for a European "Marshall Plan" to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles and reduce carbon emissions in the face of Chinese competition.
Mar 19, 2024
0
1
Greenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. Common greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. In our solar system, the atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain gases that cause greenhouse effects. Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth; without them, Earth's surface would be on average about 33°C (59°F) colder than at present.
Human activities since the start of the industrial era around 1750 have increased the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The 2007 assessment report compiled by the IPCC observed that "changes in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols, land cover and solar radiation alter the energy balance of the climate system", and concluded that "increases in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations is very likely to have caused most of the increases in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century".
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA