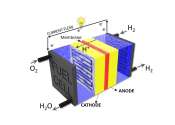
The future of hydrogen fuel: Developing a technique to analyze hydrogen fuel cell stability
Scientists at the University of New South Wales Sydney are working on ways to improve the efficiency and cost of hydrogen fuel cells, to increase access to clean fuel.
Aug 11, 2023
0
89