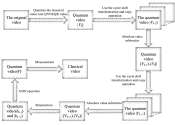
A quantum algorithm for the segmentation of a moving target in grayscale videos
Computer vision algorithms have become increasingly advanced over the past decades, enabling the development of sophisticated technologies to monitor specific environments, detect objects of interest in video footage and ...