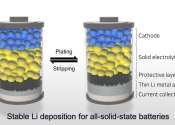
Scientists illuminate barrier to next-generation battery that charges very quickly
New lithium metal batteries with solid electrolytes are lightweight, inflammable, pack a lot of energy, and can be recharged very quickly, but they have been slow to develop due to mysterious short circuiting and failure. ...
Jan 30, 2023
2
933