US to grant Samsung up to $6.4 bn for chip plants
The United States announced on Monday grants of up to $6.4 billion to South Korean semiconductor giant Samsung to produce cutting-edge chips in Texas.
Apr 15, 2024
0
5
Business

The United States announced on Monday grants of up to $6.4 billion to South Korean semiconductor giant Samsung to produce cutting-edge chips in Texas.
Apr 15, 2024
0
5
Business

Best Buy, in a shift toward AI, laid off Geek Squad field agents, home-theater repair technicians and phone support specialists, according to current and former employees.
Apr 11, 2024
0
1
Electronics & Semiconductors

When scuba divers need to say "I'm okay" or "Shark!" to their dive partners, they use hand signals to communicate visually. But sometimes these movements are difficult to see.
Apr 10, 2024
0
45
Software

Deep learning is a form of artificial intelligence transforming society by teaching computers to process information using artificial neural networks that mimic the human brain. It is now used in facial recognition, self-driving ...
Apr 9, 2024
0
30
Computer Sciences
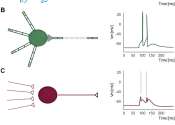
The biological brain, especially the human brain, is a desirable computing system that consumes little energy and runs at high efficiency. To build a computing system just as good, many neuromorphic scientists focus on designing ...
Apr 8, 2024
0
46
Hardware

Officials at a startup based in Carlsbad, California, expect a battery technology they have engineered will transform the way e-bikes and electric-powered hand-held tools are charged. And once it's scaled up, they believe ...
Apr 6, 2024
0
7
Electronics & Semiconductors
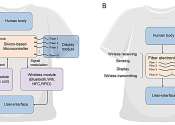
A team of materials scientists and engineers from Donghua University, in China, and the National University of Singapore, has developed a type of fiber that does not rely on chips or batteries to convert visual signals to ...
Electronics & Semiconductors

Damage to nerve tissue due to skin defects such as burns, skin diseases, and trauma causes loss of sensory and cognitive functions that are essential for life-sustaining activities, as well as mental and physical distress. ...
Apr 4, 2024
0
32
Engineering
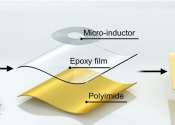
A research team has developed a mini-inductor based on amorphous alloys that can achieve both excellent flexibility and high inductance. The study is published in Advanced Functional Materials.
Apr 3, 2024
0
61
Electronics & Semiconductors
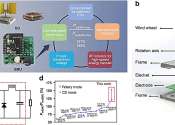
Researchers have developed a high-performance energy management unit (EMU) that significantly boosts the efficiency of electrostatic generators for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. This breakthrough addresses the challenge ...
Apr 1, 2024
0
50
The electron is a subatomic particle that carries a negative electric charge. It has no known substructure and is believed to be a point particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1836 times less than that of the proton. The intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of the electron is a half integer value of 1/2, which means that it is a fermion. The anti-particle of the electron is called the positron, which is identical to electron except that it carries electrical and other charges of the opposite sign. In collisions electrons and positrons annihilate, producing a pair (or more) of gamma ray photons. Electrons participate in gravitational, electromagnetic and weak interactions.
The concept of an indivisible amount of electric charge was theorized to explain the chemical properties of atoms, beginning in 1838 by British natural philosopher Richard Laming; the name electron was introduced for this charge in 1894 by Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney. The electron was identified as a particle in 1897 by J. J. Thomson and his team of British physicists. Electrons are identical particles that belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family. Electrons have quantum mechanical properties of both a particle and a wave, so they can collide with other particles and be diffracted like light. Each electron occupies a quantum state that describes its random behavior upon measuring a physical parameter, such as its energy or spin orientation. Because an electron is a type of fermion, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state; this property is known as the Pauli exclusion principle.
In many physical phenomena, such as electricity, magnetism, and thermal conductivity, electrons play an essential role. An electron generates a magnetic field while moving, and it is deflected by external magnetic fields. When an electron is accelerated, it can absorb or radiate energy in the form of photons. Electrons, together with atomic nuclei made of protons and neutrons, make up atoms. However, electrons contribute less than 0.06% to an atom's total mass. The attractive Coulomb force between an electron and a proton causes electrons to be bound into atoms. The exchange or sharing of the electrons between two or more atoms is the main cause of chemical bonding.
Electrons were created by the Big Bang, and they are lost in stellar nucleosynthesis processes. Electrons are produced by cosmic rays entering the atmosphere and are predicted to be created by Hawking radiation at the event horizon of a black hole. Radioactive isotopes can release an electron from an atomic nucleus as a result of negative beta decay. Laboratory instruments are capable of containing and observing individual electrons, while telescopes can detect electron plasma by its energy emission. Electrons have multiple applications, including welding, cathode ray tubes, electron microscopes, radiation therapy, lasers and particle accelerators.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA