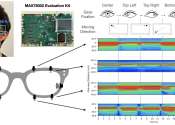
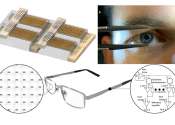
AI-powered 'sonar' on smartglasses tracks gaze, facial expressions
Cornell University researchers have developed two technologies that track a person's gaze and facial expressions through sonar-like sensing. The technology is small enough to fit on commercial smartglasses or virtual reality ...
Apr 10, 2024
0
118