Sunrise to sunset, a new window coating blocks heat, not view
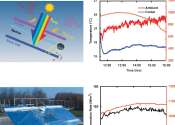
Windows welcome light into interior spaces, but they also bring in unwanted heat. A new window coating blocks heat-generating ultraviolet and infrared light and lets through visible light, regardless of the sun's angle. The ...
Apr 2, 2024
0
87