How a small 'gap' brings green energy storage through electrolysis closer
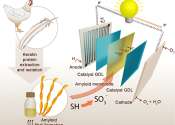
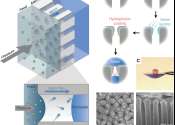
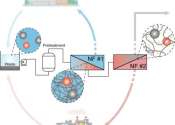
Green hydrogen is a serious contender to become a renewable energy carrier. For example, we could use it to store solar and wind energy during peaks in order to utilize the energy when the sun is no longer shining and the ...
Oct 26, 2023
0
9