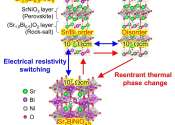
Sodium-ion batteries: How doping works
Sodium-ion batteries still have a number of weaknesses that could be remedied by optimizing the battery materials. One possibility is to dope the cathode material with foreign elements. A team from HZB and Humboldt-Universität ...
Feb 21, 2024
0
28