Clothing made from a reversible fabric could warm or cool wearers and keep them comfortable
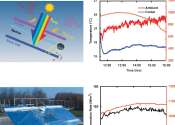
Stanford researchers have developed a reversible fabric that, without expending effort or energy, keeps skin a comfortable temperature whatever the weather.
Nov 13, 2017
0
23