A breakthrough in ceramic 3D printing
For Chinese scientists at Jiangnan University, the shape of things to come rests on a ceramic slurry and 3D printing.
Engineering

For Chinese scientists at Jiangnan University, the shape of things to come rests on a ceramic slurry and 3D printing.
Engineering

Northwestern University researchers have developed a new, futuristic 3D printer that is so big and so fast it can print an object the size of an adult human in just a couple of hours.
Oct 17, 2019
0
310
Energy & Green Tech

For generations, kids have been coaxed into finishing their vegetables after their parents sternly advised them that it is not nice to waste food when people are starving elsewhere in the world. But someday soon, kids may ...
Engineering

A team of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) researchers has designed a 'smart' device to harvest daylight and relay it to underground spaces, reducing the need to draw on traditional energy sources ...
Mar 31, 2021
1
3698
Engineering

Chances are, the screen you're reading from glows thanks to light-emitting diodes—commonly known as LEDs. This widespread technology provides energy-efficient indoor lighting and increasingly illuminates our computer monitors, ...
Aug 2, 2023
1
59
Engineering

MIT scientists have created the first completely digitally manufactured plasma sensors for orbiting spacecraft. These plasma sensors, also known as retarding potential analyzers (RPAs), are used by satellites to determine ...
Jul 27, 2022
0
278
Electronics & Semiconductors

Like the brakes that stop cars, a molecular brake exists that can prevent semiconductor chains from slipping, enabling the creation of more groundbreaking devices.
Jun 9, 2023
0
133
Engineering

LeviPrint is a system that uses acoustic manipulation for assembling objects without physical contact. It generates acoustic fields that trap small particles, glue droplets and elongated stick-like elements that can be manipulated ...
Jun 29, 2022
0
35
Engineering

A team of engineers and doctors at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have designed a unique 3D-printed light-sensing medical device that is placed directly on the skin and gives real-time feedback to correlate light ...
Sep 8, 2022
0
60
Energy & Green Tech
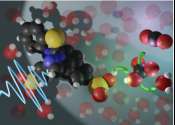
Using light instead of heat, researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have found a new way to release carbon dioxide (CO2) from a solvent used in direct air capture, or DAC, to trap this greenhouse ...
Sep 28, 2023
0
59
Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than x-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV. It is so named because the spectrum consists of electromagnetic waves with frequencies higher than those that humans identify as the color violet.
UV light is found in sunlight and is emitted by electric arcs and specialized lights such as black lights. As an ionizing radiation it can cause chemical reactions, and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Most people are aware of the effects of UV through the painful condition of sunburn, but the UV spectrum has many other effects, both beneficial and damaging, on human health.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA