Nature
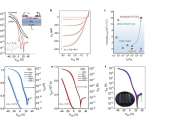
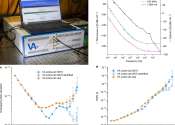
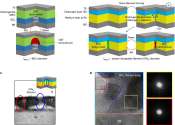
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world s most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports. Most scientific journals are now highly specialized, and Nature is among the few journals (the other weekly journals Science and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences are also prominent examples) that still publish original research articles across a wide range of scientific fields. There are many fields of scientific research in which important new advances and original research are published as either articles or letters in Nature.
Research scientists are the primary audience for the journal, but summaries and accompanying articles are intended to make many of the most important papers understandable to scientists in other fields and the educated general public. Towards the front of each issue are editorials, news and feature articles on issues of general interest to scientists, including current affairs, science funding, business, scientific ethics and research breakthroughs. There are also sections on books and arts.
- Publisher
- Nature Publishing Group
- Country
- United Kingdom
- History
- 1869-present
- Website
- http://www.nature.com/nature/index.html
- Impact factor
- 36.101 (2010)
Some content from Wikipedia,
licensed under CC BY-SA