AI radar system that can spot miniature drones 3 kilometers away
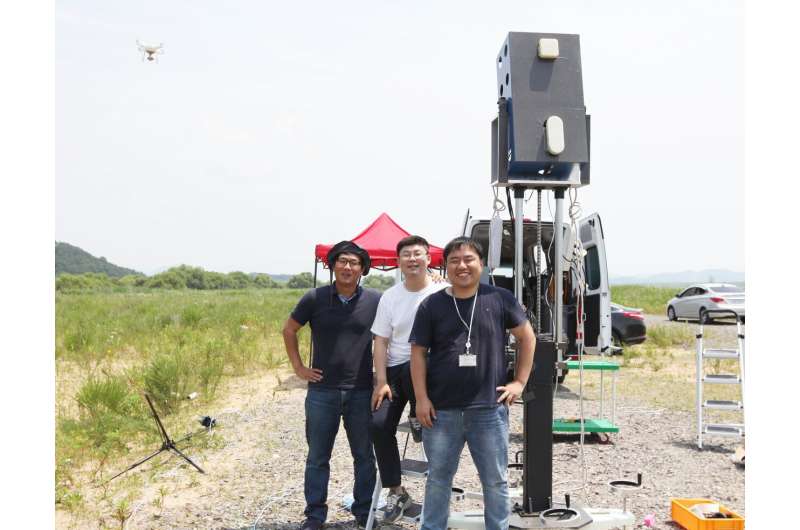

DGIST announced on Tuesday, July 16 that Senior Researcher Dae-gun Oh's team in the Collaborative Robots Research Center developed a radar system that can detect subminiature drones that are 3km away. This research is expected to make huge contributions to strengthening domestic industries and defense capabilities by securing a world-class radar sensing technology.
As a result of discovering a North Korean drone in Paju in March 2014, South Korea's Ministry of National Defense has adopted a drone detection radar based on overseas technology. Since last year, the ministry has devoted itself to building a combat system using drones and training specialized personnel by forming a drone unit to strengthen its defense capability. The necessity of enemy surveillance reconnaissance and the early detection of offensive drones has increased in Korea.
Due to the lack of radar detection technology, however, South Korea is using many radar systems from abroad such as drone detection radars from RADA in Israel and Blighter in the U.K. RADA owns a superior radar technology that can detect drones that are a maximum of 3km away.
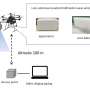
Since 2014, DGIST Senior researcher Daegun Oh's team has continuously been working on R&D of a drone detection radar system based on a super-resolution algorithm using only Korean technology and developed Korea's first radar system that can detect drones 200m away for the first time in 2016. Through continuous research, the team successfully developed a world-class radar system that can detect subminiature phantom drones flying in the sky over 3km.
The research team designed the drone detection radar system to operate between 12GHz and 18GHz, and applied super-resolution radar signal processing technology to locate drones accurately by applying an AESA radar1 technology to increase the maximum detection distance of radar. Furthermore, the radar system can identify and detect drones more clearly in real-time by integrating GAN (Generative Adversarial Networks) based drone cognition technology, which has been drawing attention as a next generation deep learning algorithm.
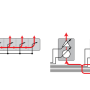
What is noteworthy is that hardware components such as the transmission, transmission antenna, receiving unit, receiving antenna, and signal processing platform inside the radar detection system were developed 100% jointly with Korean small and medium-sized companies, which can help create high added value for regional industries.
Senior researcher Daegun Oh's team in the DGIST Collaborative Robots Research Center said "This research achievement is a result of cooperation with Korean companies to develop radar hardware and our focus on the development of a unique radar signal processing algorithm for detection, tracking, and identification of drones. We will strive to enhance the reputation of domestic radar technologies in the global market by changing the market spectrum led by overseas companies." The research team is currently discussing the issue of drone detection radar technology transfer to Korean and overseas defense industries.
The AI radar identification technology in this research achievement was published in the world-class radar journal IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters on June 18. Also, papers on the elemental technology of drones have also been published in Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, IEEE Sensors, IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronics Systems, MDPI Sensors, etc.
More information: Ibrahim Alnujaim et al, Generative Adversarial Networks for Classification of Micro-Doppler Signatures of Human Activity, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters (2019). DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2919770