Washing dishes with superheated steam more effective, earth-friendly
Conventional dishwashers often do not kill all the harmful microorganisms left on plates, bowls, and cutlery. They also require long cycle times that use large quantities of electricity, and the soap pumped in and out is released into water sources, polluting the environment.
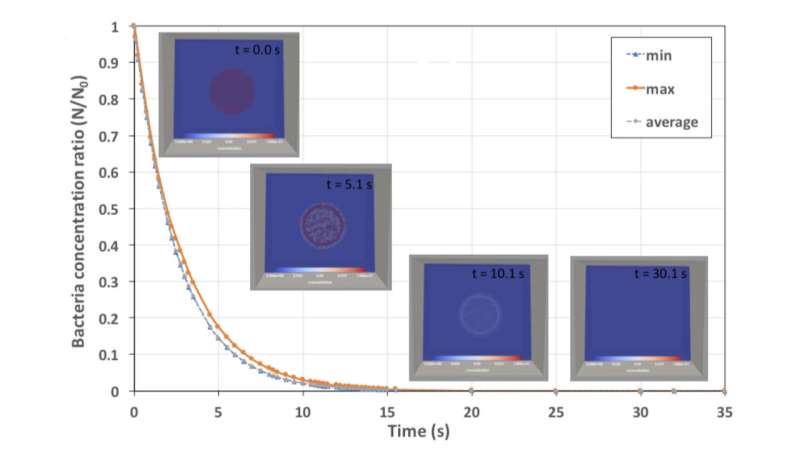
Superheated steam dishwashers could provide a more effective, environmentally friendly solution. In Physics of Fluids, researchers from the Technical University of Dortmund and the Technical University of Munich simulated such a dishwasher, finding that it killed 99% of bacteria on a plate in just 25 seconds.
The model of an idealized dishwasher looks like a box with solid side walls, a top opening, and a nozzle at the bottom. A plate covered with a heat-resistant strain of bacteria is placed directly above the nozzle. Once the plate reaches a certain threshold temperature in the simulation, the microorganisms are deemed inactivated.
"Steam comes out of the nozzle at a very high velocity. We can see shocks, and the turbulent flow that is created has eddies and vortices," said author Natalie Germann, of the Technical University of Dortmund. "We also include heat transfer, which shows how the heat changes in the simulation box and the condensation on the solid surfaces."
The shock waves, created by the high velocity of the steam, are reflected at surfaces in the dishwasher. While the team focused on bacteria in this work, the shocks could be used to effectively remove food debris in the future.
"Our study helps determine the strength of the shocks, the position of the shocks, and the vortices that are created inside the dishwasher," said author Laila Abu-Farah, of the Technical University of Munich. "These things are very important for arranging the items or objects inside the dishwasher and the placement and orientation of the nozzles."
While the simulations show quick inactivation of the bacteria, actual applications of the dishwasher would include more than one plate and therefore require more time. However, the researchers believe it would still be much faster and more effective than conventional technology.
The superheated steam dishwasher would initially cost more but would pay off in the long run with savings on water, electricity, and detergent. It would be ideal for use in restaurants, hotels, and hospitals, which must meet high hygienic standards.
"We confirmed that the dishwasher application using superheated steam is promising," said Germann. "This is the first work combining fluid dynamics and heat transfer with phase change and bacterial inactivation. It thus lays the foundation for future computational research and further technical work."
The article "Simulations of thermal phase changes and bacterial inactivation in a superheated steam dishwasher" is authored by Laila Abu-Farah and Natalie Germann. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on August 30, 2022.
More information: Simulations of thermal phase changes and bacterial inactivation in a superheated steam dishwasher, Physics of Fluids (2022). DOI: 10.1063/5.0090418