October 31, 2022 report
Incorporating nanoparticles into a porous hydrogel to propel an aquabot with minimal voltage
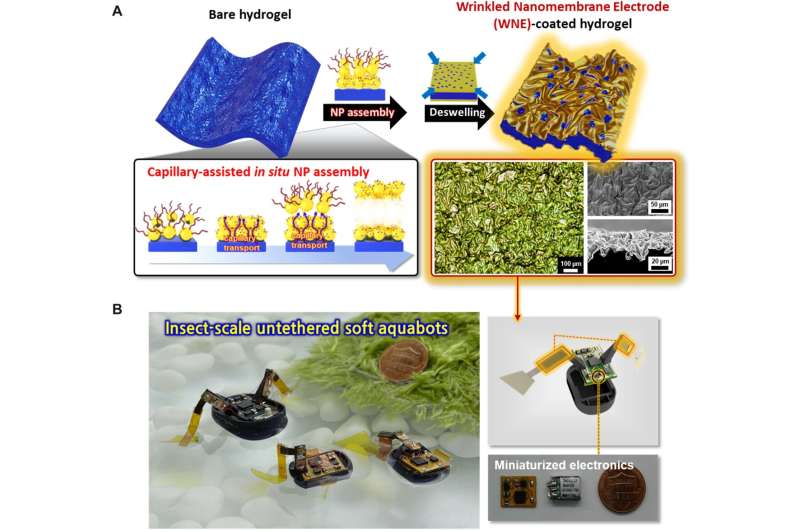
A team of researchers from Korea University, Ajou University and Hanyang University, all in the Republic of Korea, has created a tiny aquabot propelled by fins made of a porous hydrogel imbued with nanoparticles. In their paper published in the journal Science Robotics, the group describes how the hydrogel works to power a tiny boat and reveals how much voltage was required.
Scientists and engineers have been working for several years to build tiny, soft robots for use in medical applications and have found that hydrogels are quite suitable for the task. Unfortunately, such materials also have undesirable characteristics, most notably, poor electro-connectivity. In this new effort, the researchers took a new approach to making hydrogels more amenable for use with electricity as a power source—adding conductive nanoparticles.
The work involved adding a small number of nanoparticles to a part of a porous hydrogel which they then used as a wrinkled nanomembrane electrode (WNE) actuator. Adding the nanoparticles allowed the hydrogel to conduct electricity in a reliable way. Testing showed the actuator could be powered with as little as 3 volts of electricity. The researchers then fashioned two of the actuators into finlike shapes and attached them to a tiny plastic body. Electronics added to the body controlled the electricity sent to the fins. The resulting robot had a water bug appearance, floating on the surface of the water in a tank.
The actuator worked via electricity transmitted to the electrodes in the fins that were sandwiched in the hydrogel. This resulted in the creation of an electroosmotic water flow inside of a small part of the hydrogel, which in turn controlled the amount of swelling. As the hydrogel swelled, it changed the shape of the fin, resulting in a pushing force that moved the tiny aquabot on the surface of the water. The researchers note that the actuators had an energy density that was greater than 7 x 105 joules per cubic meter.
More information: Jongkuk Ko et al, High-performance electrified hydrogel actuators based on wrinkled nanomembrane electrodes for untethered insect-scale soft aquabots, Science Robotics (2022). DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.abo6463
© 2022 Science X Network