This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists propose parallel planar heterojunction strategy for efficient solar cells
Recently, a research team has put forward an intriguing approach to enhance the efficiency of solar cells. Their focus on the potential antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) as a photovoltaic absorber has led to a parallel planar heterojunction (PPHJ) strategy for the preparation of highly efficient solar cells.
Their findings have been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The researchers were led by Prof. Wang Mingtai from the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
One of the current challenges in the terrestrial utility of photovoltaic electricity is the absence of low-cost, efficient, and stable materials as well as the related photovoltaic devices for converting photons to electrons. Typically, two independent planar heterojunction (PHJ) subcells are stacked in tandem to create efficient solar cells. However, the need for an interfacial layer for the recombination of opposite charges from the top and bottom subcells increases complexity to material selection and device preparation.
"This is why we introduced the PPHJ strategy in our research," Prof. Chen Chong explains, "it enables us to tap into the practical potential of creating efficient multiple PHJ solar cells."
-

Scientists propose parallel planar heterojunction strategy for efficient solar cells. Credit: HFIPS -
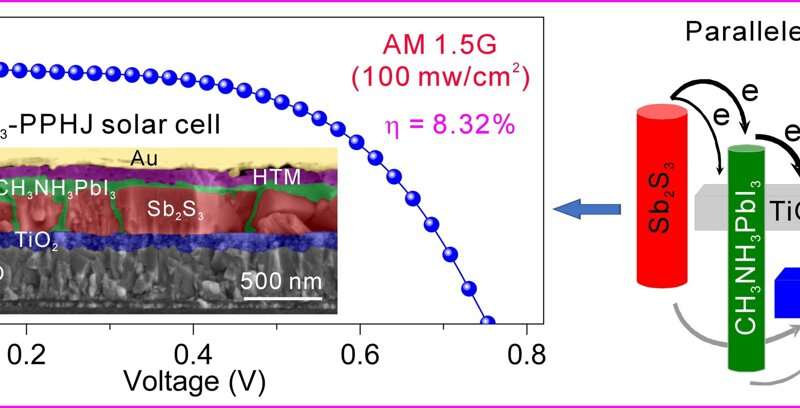
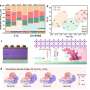
The architecture, photovoltaic performance and carrier process in the Sb2S3-based PPHJ solar cell. Credit: HFIPS
The Sb2S3-based PPHJ device consists of two types of conventional PHJ subcells connected in parallel. The Sb2S3-based PHJ subcells are responsible for absorption and charge generation, while the CH3NH3PbI3-based PHJ subcells govern the electron transport towards collection electrode. Despite the two types of subcells, the PPHJ device remains an Sb2S3 device in nature.
The outcome is a remarkable increase in the efficiency of solution-processed Sb2S3 solar cells, achieving an impressive 8.32% efficiency, the highest among all Sb2S3 devices.
"Indeed, our strategy simplifies the preparation process by allowing for the conventional sequential depositions of multiple PHJ layers," said Chen. "It eliminates the typical complexity associated with both tandem and parallel tandem PHJ systems."
"This study paves the way for the conceptual design of low-cost and efficient partially or fully inorganic solar cells, thus promoting their development," added Chen.
More information: Liangxin Zhu et al, Parallel Planar Heterojunction Strategy Enables Sb2S3 Solar Cells with Efficiency Exceeding 8%, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2023). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202312951