This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Artificial intelligence can predict events in people's lives, researchers show
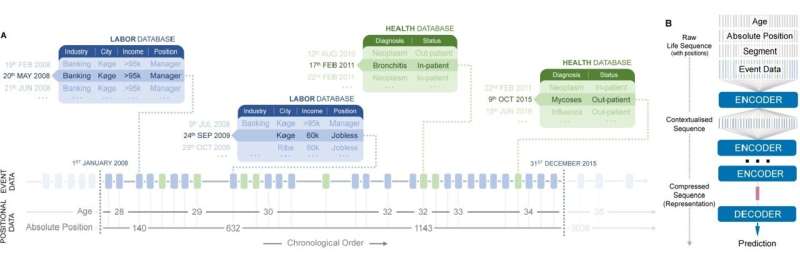
Artificial intelligence developed to model written language can be utilized to predict events in people's lives. A research project from DTU, University of Copenhagen, ITU, and Northeastern University in the US shows that if you use large amounts of data about people's lives and train so-called 'transformer models', which (like ChatGPT) are used to process language, they can systematically organize the data and predict what will happen in a person's life and even estimate the time of death.
In a new article, "Using Sequences of Life-events to Predict Human Lives," published in Nature Computational Science, researchers have analyzed health data and attachment to the labor market for 6 million Danes in a model dubbed life2vec.
After the model has been trained in an initial phase, i.e., learned the patterns in the data, it has been shown to outperform other advanced neural networks and predict outcomes such as personality and time of death with high accuracy.
"We used the model to address the fundamental question: to what extent can we predict events in your future based on conditions and events in your past? Scientifically, what is exciting for us is not so much the prediction itself, but the aspects of data that enable the model to provide such precise answers," says Sune Lehmann, professor at DTU and first author of the article.
Predictions of time of death
The predictions from Life2vec are answers to general questions such as: 'death within four years'? When the researchers analyze the model's responses, the results are consistent with existing findings within the social sciences; for example, all things being equal, individuals in a leadership position or with a high income are more likely to survive, while being male, skilled or having a mental diagnosis is associated with a higher risk of dying.
Life2vec encodes the data in a large system of vectors, a mathematical structure that organizes the different data. The model decides where to place data on the time of birth, schooling, education, salary, housing, and health.
"What's exciting is to consider human life as a long sequence of events, similar to how a sentence in a language consists of a series of words. This is usually the type of task for which transformer models in AI are used, but in our experiments, we use them to analyze what we call life sequences, i.e., events that have happened in human life," says Sune Lehmann.
Raising ethical questions
The researchers behind the article point out that ethical questions surround the life2vec model, such as protecting sensitive data, privacy, and the role of bias in data. These challenges must be understood more deeply before the model can be used, for example, to assess an individual's risk of contracting a disease or other preventable life events.
"The model opens up important positive and negative perspectives to discuss and address politically. Similar technologies for predicting life events and human behavior are already used today inside tech companies that, for example, track our behavior on social networks, profile us extremely accurately, and use these profiles to predict our behavior and influence us. This discussion needs to be part of the democratic conversation so that we consider where technology is taking us and whether this is a development we want," says Sune Lehmann.
According to the researchers, the next step would be to incorporate other types of information, such as text and images or information about our social connections. This use of data opens up a whole new interaction between social and health sciences.
More information: Sune Lehmann, Using sequences of life-events to predict human lives, Nature Computational Science (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s43588-023-00573-5. www.nature.com/articles/s43588-023-00573-5