This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Real-time multimodal tactile detection system applicable to robots and wearable devices
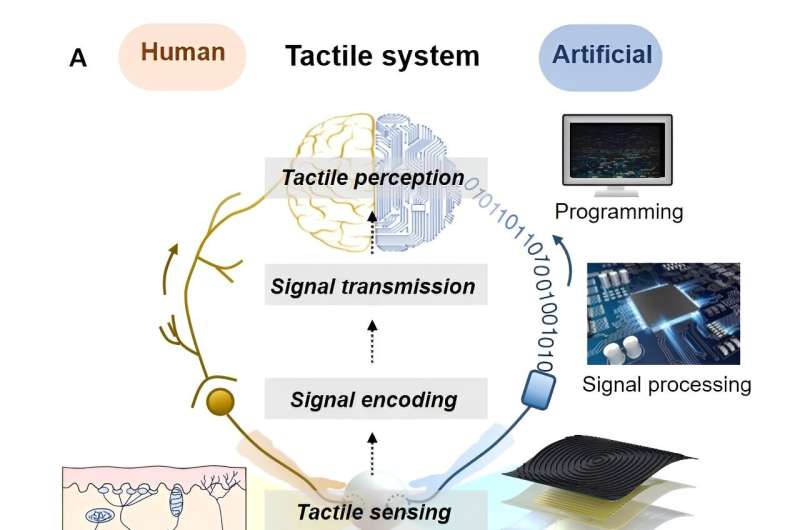
A tactile perception system capable of providing human-like multimodal tactile information to objects like robots and wearable devices that require tactile data in real-time has been developed.
The researchers developed a real-time and multimodal tactile perception system capable of providing multi-tactile information in real-time inspired by human tactile perception, and announced the outcome of the research in Soft Robotics.
The research team developed a real-time and multimodal tactile detection system by mimicking the principle by which various types of tactile information are perceived by a variety of sensory receptors in the human skin and transmitted to the brain in real time.
This system consists of four three-dimensional stacked tactile sensors, a signal processing/transmission module, and an analysis module. The system has successfully distinguished various types of tactile stimuli and surface textures and, furthermore, differentiated complex motion in real-time.
Four types of tactile sensors, each of which detects temperature, vibration, shear force, and vertical pressure, are laminated in a three-dimensional structure based on three-dimensional (3D) flexible electrode printing process technology.
At the same time, these sensors are connected to the FPCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board) of the electronic module for signal processing and transmission, thereby easily transmitting signal-processed tactile information through the corresponding FPCB connection terminal.
In previous studies, complex external measuring devices and analysis equipment were needed in order to detect the signals generated from the corresponding device so that various forms of tactile stimuli could be detected. Therefore, it was difficult to apply these devices to wearable devices or robots in the form of a simple stand-alone system.
-
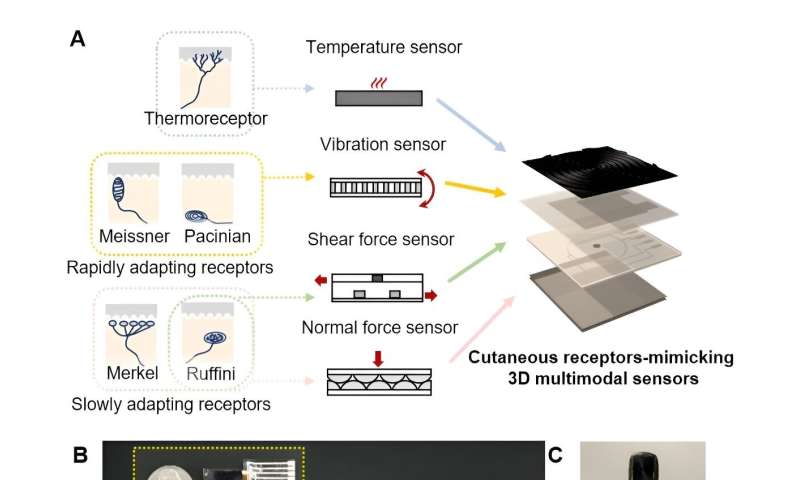
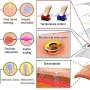
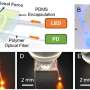
Cutaneous receptors-mimicking sensors. (A) Schematics of the cutaneous receptors and proposed multimodal sensors. (B) Photographs of the 3D integrated sensors connected to the flexible 3D interconnection system. (C) Photograph of the 3D integrated sensors mounted on a robotic finger. The scale bars show 1 cm. Credit: Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) -
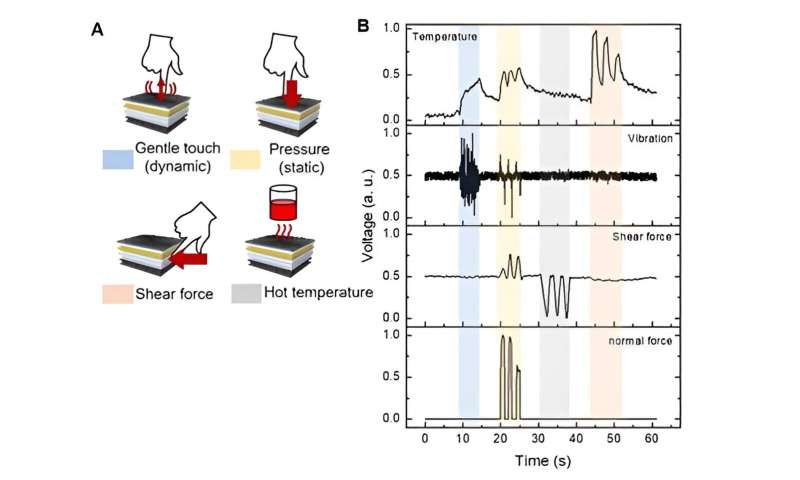
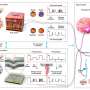
Real-time and simultaneous monitoring for various tactile stimuli. (A) Illustrations for the four kinds of physical stimuli applied. The colored squares next to the stimuli in the graph indicate the region where the stimuli occurred. (B) Electrical responses for various physical stimuli. Credit: Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) -
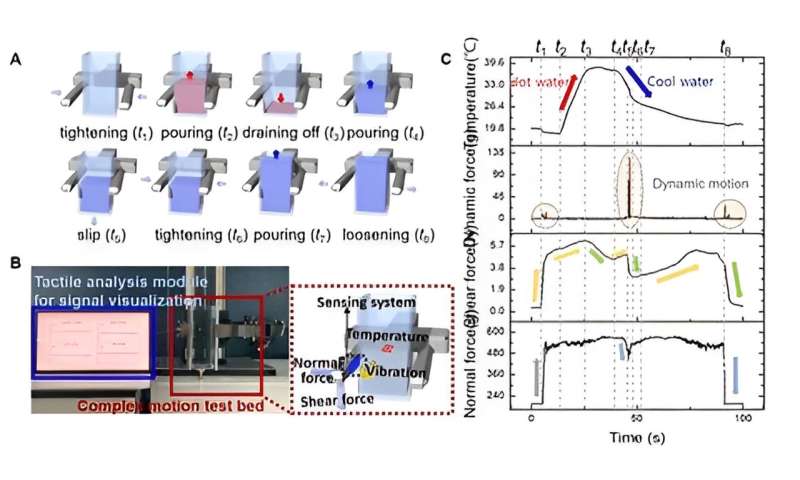
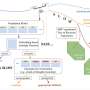
Perception of complex tactile motion. (A) Illustrated images for eight kinds of consecutive operations. (B) Photograph and image of the experimental setup for complex motion test. (C) The transformed signals for the complex tactile motion using a real-time, simultaneous and continuous sensing system. Credit: Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM)
On the other hand, in the newly developed multimodal tactile perception system, multiple types of tactile sensors are arranged vertically in a three-dimensional structure. Additionally, a module capable of converting, transmitting, and analyzing the signals has also been developed, which allows for the system to be implemented in a compact and simple form and makes it applicable to actual robots and wearable devices.
The research team was led by Research Director Hyuneui Lim of the Nano-Convergence Manufacturing Systems Research Division and Principal Researcher Youngdo Jung of the Department of Nature-Inspired System and Application of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials, an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Lim said, "By mimicking the sensory system of humans, the real-time multimodal tactile perception system is capable of perceiving multiple senses simultaneously. Moreover, it is a technology that has solved the problems that may be caused by complex and large signal processing and detection systems when using conventional sensors."
"By applying this system to robots or wearable devices, we will be able to obtain a large volume of diverse and complex tactile signal information, which will hopefully contribute to the improvement of public welfare and security."
More information: Bo-Yeon Lee et al, Human-Inspired Tactile Perception System for Real-Time and Multimodal Detection of Tactile Stimuli, Soft Robotics (2023). DOI: 10.1089/soro.2022.0191