This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Sodium-ion batteries: How doping works
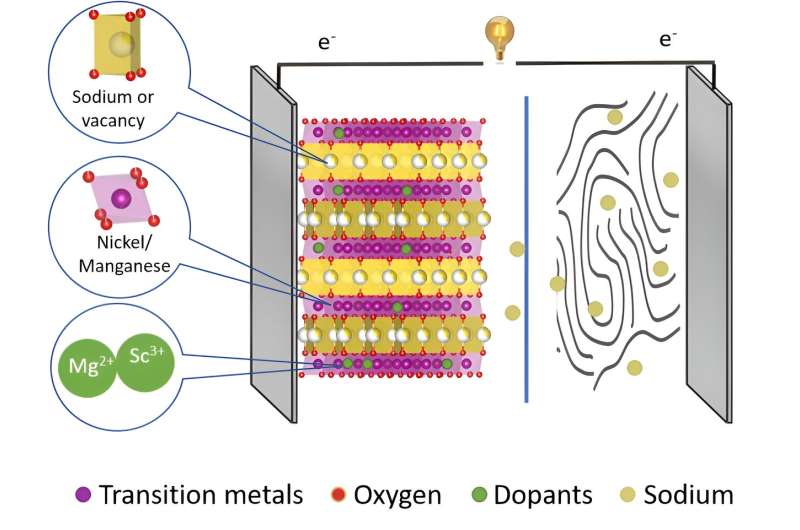
Sodium-ion batteries still have a number of weaknesses that could be remedied by optimizing the battery materials. One possibility is to dope the cathode material with foreign elements. A team from HZB and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has now investigated the effects of doping with scandium and magnesium.
The scientists collected data at the X-ray sources BESSY II, PETRA III, and SOLARIS to get a complete picture and uncovered two competing mechanisms that determine the stability of the cathodes. Their research is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIB) have the highest possible energy density per kilogram, but lithium resources are limited. Sodium, on the other hand, has a virtually unlimited supply and is the second-best option in terms of energy density. Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) would therefore be a good alternative, especially if the weight of the batteries is not a major concern, for example in stationary energy storage systems.
However, experts are convinced that the capacity of these batteries could be significantly increased by a targeted material design of the cathodes. Cathode materials made of layered transition metal oxides with the elements nickel and manganese (NMO cathodes) are particularly promising.
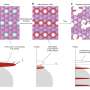
They form host structures in which the sodium ions are stored during discharge and released again during charging. However, there is a risk of chemical reactions which may initially improve the capacity, but ultimately degrade the cathode material through local structural changes. This has the consequence of reducing the lifetime of the sodium-ion batteries.
"But we need high capacity with high stability," says Dr. Katherine Mazzio, who is a member of the joint research group Operando Battery Analysis at HZB and the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, headed by Prof Philipp Adelhelm. Spearheaded by Ph.D. student Yongchun Li, they have now investigated how doping with foreign elements affects the NMO cathodes.
Different elements were selected as dopants that have similar ionic radii to nickel (Ni 2+), but different valence states: magnesium (Mg 2+) ions or scandium ions (Sc 3+).
Three years of experiments at BESSY II, PETRA III, and SOLARIS
To decipher the influence of the two elements, they had to carry out experiments at three different X-ray sources.
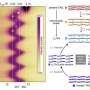
At BESSY II, they analyzed the samples using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) in the soft and hard X-ray ranges; at PETRA III, they evaluated structural changes with X-ray diffraction (XRD) and pair distribution function analysis (PDF) with hard X-rays, and for more detailed insights on the element magnesium, they carried out additional soft XAS investigations at the PIRX beamline at SOLARIS.
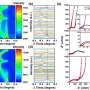
"The results surprised us," explains Mazzio. Although doping with scandium leads to fewer structural changes during the electrochemical cycle than doping with magnesium, it does not improve stability. "Until now, it was thought that suppressing phase transitions (and thus volume changes) would also improve the cathode material cycling performance over many cycles. But that's not enough."
Magnesium doping suppresses the oxygen redox reaction in NMO even more. This was also unexpected, as magnesium is known to trigger an oxygen redox reaction in layered manganese oxides. "We analyzed different Mg/Ni ratios in NMO and found that the oxygen redox reaction reaches a minimum at a ratio close to 1," explains Mazzio.
"Only through a combination of advanced X-ray techniques could we show that it is more than just suppression phase transitions that are important for improving the long-term cycling behavior, but also the interplay between Ni and O redox activity dictate performance."
More information: Yongchun Li et al, Competing Mechanisms Determine Oxygen Redox in Doped Ni–Mn Based Layered Oxides for Na‐Ion Batteries, Advanced Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202309842