Algae offer real potential as a renewable electricity source, research shows
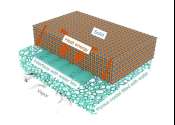
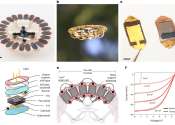
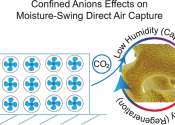
The need to transition away from fossil fuels to more sustainable energy production is critical. That's why a team of Concordia researchers is looking at a potential power source that not only produces no carbon emissions ...
Jun 11, 2024
0
83