Telescope: a tool to manage bioinformatics analyses on mobile devices
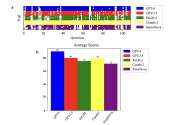
A team of researchers at UCLA, the University of São Paulo, the Federal University of São Carlos and the University of Southern California has recently developed an interactive tool for managing large-scale bioinformatic ...