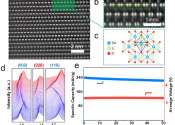
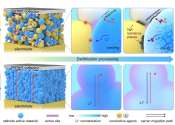
A strategy to suppress strain propagation in ultrahigh-Ni cathodes during fast charging
To meet the growing demand of the electronics industry and support the widespread deployment of electric vehicles, researchers will need to develop increasingly advanced and highly performing battery technologies. A promising ...