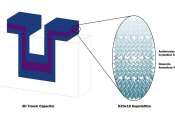
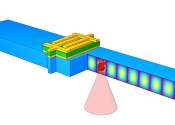
A new approach to prepare solution-processable 2-D semiconductors
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the University of Texas at Austin, and Hunan University (China) have recently devised a new method of preparing highly uniform, solution-processable, phase-pure ...