Unbroken: New soft electronics don't break, even when punctured
Want a smartphone that stretches, takes damage, and still doesn't miss a call?
Jun 26, 2021
0
145
Electronics & Semiconductors

Want a smartphone that stretches, takes damage, and still doesn't miss a call?
Jun 26, 2021
0
145
Electronics & Semiconductors

Electronic organic materials offer promise to support alternative and green energy sources to meet escalating global energy demands and strict environmental regulations. A KAUST-led team has now developed electron-transporting, ...
Mar 17, 2021
0
112
Electronics & Semiconductors

More precise, faster, cheaper: Researchers all over the world have been working for years on producing electrical circuits using additive processes such as robotic 3D-printing (so-called robocasting) with great success, but ...
Dec 20, 2021
0
177
Energy & Green Tech

Scientists have discovered a stable and highly conductive lithium-ion conductor for use as solid electrolytes for solid-state lithium-ion batteries.
Apr 2, 2024
0
71
Electronics & Semiconductors

A soft and flexible electronic "e-skin," so sensitive it can detect the minute temperature difference between an inhaled and an exhaled breath, could form the basis of a new form of on-skin biosensor. The ultrathin material ...
Nov 29, 2022
0
85
Electronics & Semiconductors
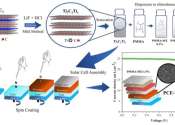
In an article published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry C, Brazilian researchers describe a strategy to enhance the efficiency and stability of solar cells made of perovskite, a semiconductor material produced in the ...
Feb 26, 2024
0
29
Machine learning & AI

A research team has demonstrated that analog hardware using ECRAM devices can maximize the computational performance of artificial intelligence, showcasing its potential for commercialization. Their research has been published ...
Aug 1, 2024
0
30
Engineering

Several industrial, automotive and health care applications rely on accurate and precise measurement of pressure. Flexible and wearable pressure sensors are typically fabricated using petroleum-based polymers. The solid waste ...
Sep 20, 2022
0
29
Energy & Green Tech

North Carolina State University engineers have demonstrated a flexible device that harvests the heat energy from the human body to monitor health. The device surpasses all other flexible harvesters that use body heat as the ...
Jan 30, 2020
0
84
Electronics & Semiconductors

Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new, more environmentally friendly way to create conductive inks for use in organic electronics such as solar cells, artificial neurons, and soft sensors. The ...
Jan 22, 2024
0
101
Electrical conductivity or specific conductance is a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current. When an electrical potential difference is placed across a conductor, its movable charges flow, giving rise to an electric current. The conductivity σ is defined as the ratio of the current density to the electric field strength :
It is also possible to have materials in which the conductivity is anisotropic, in which case σ is a 3×3 matrix (or more technically a rank-2 tensor) which is generally symmetric.
Conductivity is the reciprocal (inverse) of electrical resistivity, ρ, and has the SI units of siemens per metre (S·m-1):
Electrical conductivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter σ, but κ (esp. in electrical engineering science) or γ are also occasionally used.
An EC meter is normally used to measure conductivity in a solution.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA