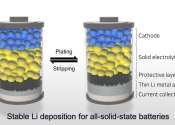
New advance in all-solid-state battery technology enhances performance of lithium from the bottom
A research team has successfully enhanced the performance and durability of all-solid-state batteries. This breakthrough was made possible through the implementation of a novel approach known as bottom electrodeposition. ...
Mar 14, 2024
0
63