Adding thin layer of tin prevents short-circuiting in lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have a lot of advantages. They charge quickly, have a high energy density, and can be repeatedly charged and discharged.
Jul 31, 2024
0
48
Energy & Green Tech

Lithium-ion batteries have a lot of advantages. They charge quickly, have a high energy density, and can be repeatedly charged and discharged.
Jul 31, 2024
0
48
Energy & Green Tech

Strong offshore winds have the potential to supply coastlines with massive, consistent flows of clean electricity. One study estimates offshore wind farms could meet 11 times the projected global electricity demand in 2040.
Jul 31, 2024
0
1
Consumer & Gadgets

As artificial intelligence (AI) technologies become more embedded into our everyday lives and business operations, their high energy demands and environmental impacts call for a more sustainable approach to building algorithms—the ...
Jul 31, 2024
0
5
Energy & Green Tech

Many people now work partly or permanently from home. This saves petrol because they no longer have to drive to the office—which is good for the energy transition. Or not. Because at home, they consume even more energy ...
Jul 31, 2024
0
8
Energy & Green Tech
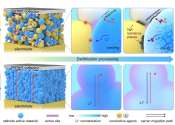
Researchers at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from leading international institutions, have introduced an innovative cathode ...
Jul 31, 2024
0
82
Energy & Green Tech

The combined thermal degradation of olive pomace and plastic waste by pyrolysis increases the effectiveness of the process and generates new value-added products, such as biofuels, according to a study by the University of ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
11
Energy & Green Tech

Solar energy is one of humanity's best bets against the ongoing energy crises and climate change. With solar panels becoming an attractive energy solution, both in open fields and on rooftops in urban areas, scientists are ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
15
Engineering

Most wind turbines face the wind—and there is a good reason for that. Since the 1980s, wind turbine developers have been using what is called the "Danish concept" for their designs—three blades, positioned upwind (i.e., ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
2
Energy & Green Tech

With their massive sails stretched over towering masts, merchant ships that plied the world's oceans hundreds of years ago helped launch the era of commercial shipping, delivering goods of all kinds to different ports of ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
4
Energy & Green Tech

Our insatiable demand for digital content and services has been driving a rise in energy-hungry data centers.
Jul 29, 2024
0
11
In physics, energy (from the Greek ἐνέργεια - energeia, "activity, operation", from ἐνεργός - energos, "active, working") is a scalar physical quantity that describes the amount of work that can be performed by a force, an attribute of objects and systems that is subject to a conservation law. Different forms of energy include kinetic, potential, thermal, gravitational, sound, light, elastic, and electromagnetic energy. The forms of energy are often named after a related force.
Any form of energy can be transformed into another form, but the total energy always remains the same. This principle, the conservation of energy, was first postulated in the early 19th century, and applies to any isolated system. According to Noether's theorem, the conservation of energy is a consequence of the fact that the laws of physics do not change over time.
Although the total energy of a system does not change with time, its value may depend on the frame of reference. For example, a seated passenger in a moving airplane has zero kinetic energy relative to the airplane, but non-zero kinetic energy relative to the Earth.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA