Biofuel from kudzu vines and branches boosts energy efficiency
Leftover branches and kudzu vines from logging are repurposed as carbon-neutral fuel to generate electricity.
Jun 26, 2024
0
1
Energy & Green Tech

Leftover branches and kudzu vines from logging are repurposed as carbon-neutral fuel to generate electricity.
Jun 26, 2024
0
1
Energy & Green Tech

It seems like energy policies are constantly making headlines these days. Should Canada "axe the tax?" Is it time to end the tax breaks to Canadian fossil fuel companies and invest in renewable energy? Are electric vehicles ...
Jun 22, 2024
0
2
Energy & Green Tech
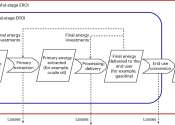
Energy researchers have been trying to understand the implications of a transition to fully renewable energy for decades. Some past studies suggested that technologies to generate energy from renewable energy sources, such ...
Business

This week's announcement of the government's plans to reopen New Zealand's territorial waters to oil drilling comes as no surprise. All three coalition parties campaigned on reversing the 2018 ban on offshore oil exploration.
Jun 13, 2024
0
8
Engineering

The need to transition away from fossil fuels to more sustainable energy production is critical. That's why a team of Concordia researchers is looking at a potential power source that not only produces no carbon emissions ...
Jun 11, 2024
0
83
Energy & Green Tech

Green hydrogen could transform our energy system and solve many supply and emissions challenges. Whether this happens will depend on how economically it can be produced and how attractive it will be to consumers.
Jun 10, 2024
0
21
Energy & Green Tech

More money is pouring into solar power than all other electricity sources combined, with investments set to reach half a trillion dollars this year, the world's top energy research body said Thursday.
Jun 6, 2024
0
32
Energy & Green Tech

Nations are falling short of the goal agreed at UN climate talks to triple renewable energy capacity by 2030 as part of efforts to curb global warming, the International Energy Agency said Tuesday.
Jun 4, 2024
0
16
Energy & Green Tech

The energy transition is not on track to mitigate the effects of climate change. Take the case of Shell, whose shareholders recently voted to decelerate the UK-based oil giant's climate targets. Shell had planned to cut its ...
Jun 3, 2024
0
1
Energy & Green Tech

Chile's state-owned copper giant Codelco signed a deal Friday with SQM to nearly double the private mining firm's current extraction of lithium, a key mineral for the global switch to cleaner energy.
May 31, 2024
0
27
Fossil fuels or mineral fuels are fuels formed by natural resources such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years. These fuels contain high percentage of carbon and hydrocarbons.
Fossil fuels range from volatile materials with low carbon:hydrogen ratios like methane, to liquid petroleum to nonvolatile materials composed of almost pure carbon, like anthracite coal. Methane can be found in hydrocarbon fields, alone, associated with oil, or in the form of methane clathrates. It is generally accepted that they formed from the fossilized remains of dead plants and animals by exposure to heat and pressure in the Earth's crust over hundreds of millions of years. This biogenic theory was first introduced by Georg Agricola in 1556 and later by Mikhail Lomonosov in the 18th century.
It was estimated by the Energy Information Administration that in 2006 primary sources of energy consisted of petroleum 36.8%, coal 26.6%, natural gas 22.9%, amounting to an 86% share for fossil fuels in primary energy production in the world. Non-fossil sources included hydroelectric 6.3%, nuclear 6.0%, and (geothermal, solar, tide, wind, wood, waste) amounting 0.9 percent. World energy consumption was growing about 2.3% per year.
Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources because they take millions of years to form, and reserves are being depleted much faster than new ones are being formed. The production and use of fossil fuels raise environmental concerns. A global movement toward the generation of renewable energy is therefore under way to help meet increased energy needs.[citation needed]
The burning of fossil fuels produces around 21.3 billion tonnes (21.3 gigatonnes) of carbon dioxide per year, but it is estimated that natural processes can only absorb about half of that amount, so there is a net increase of 10.65 billion tonnes of atmospheric carbon dioxide per year (one tonne of atmospheric carbon is equivalent to 44/12 or 3.7 tonnes of carbon). Carbon dioxide is one of the greenhouse gases that enhances radiative forcing and contributes to global warming, causing the average surface temperature of the Earth to rise in response, which climate scientists agree will cause major adverse effects.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA