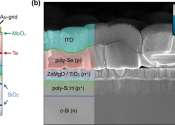
The world's largest 3D printer is at a university in Maine. It just unveiled an even bigger one
The world's largest 3D printer has created a house that can cut construction time and labor. An even larger printer unveiled on Tuesday may one day create entire neighborhoods.
Apr 23, 2024
0
27