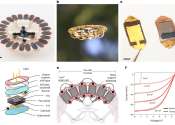
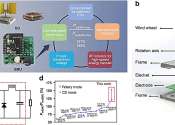
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standardized Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private and public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope that are linked by copper wires, fiber-optic cables, wireless connections, and other technologies.
The Internet carries a vast array of information resources and services, most notably the inter-linked hypertext documents of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the infrastructure to support electronic mail, in addition to popular services such as online chat, file transfer and file sharing, online gaming, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) person-to-person communication via voice and video.
The origins of the Internet reach back to the 1960s when the United States funded research projects of its military agencies to build robust, fault-tolerant and distributed computer networks. This research and a period of civilian funding of a new U.S. backbone by the National Science Foundation spawned worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and led to the commercialization of an international network in the mid 1990s, and resulted in the following popularization of countless applications in virtually every aspect of modern human life. By 2009, an estimated quarter of Earth's population uses the services of the Internet (see Growth).