Methane emissions from landfill could be turned into sustainable jet fuel with plasma-driven process
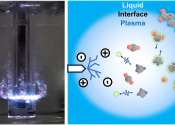
In a world first, University of Sydney researchers have developed a chemical process using plasma that could create sustainable jet fuel from methane gas emitted from landfills, potentially creating a low-carbon aviation ...
Apr 30, 2024
0
51