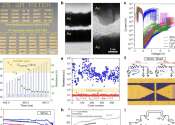
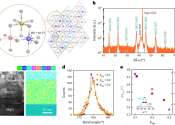
Memristive radiofrequency switches show improved performance for mmWave applications
Radiofrequency (RF) switches are electronic components that control the routing of RF signals between different segments of circuits, for instance turning the signals on and off or redirecting them. These switches are central ...