Fighting food waste: New system uses wireless signals in the sub-terahertz band to determine fruit ripeness
One bad apple may not spoil the whole bunch, but when it comes to distributing food, a lot of good goes out with the bad.
Oct 4, 2023
0
42
Engineering

One bad apple may not spoil the whole bunch, but when it comes to distributing food, a lot of good goes out with the bad.
Oct 4, 2023
0
42
Internet

We've heard it for years: 5G is coming.
Feb 4, 2020
6
309
Telecom
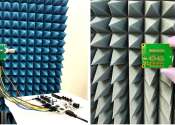
A team led by researchers from the University of Glasgow has developed an innovative wireless communications antenna that combines the unique properties of metamaterials with sophisticated signal processing to deliver a new ...
Apr 12, 2024
0
104
Consumer & Gadgets
Researchers from Singapore say they have found security flaws in more than 480 Bluetooth devices including smart home gadgets, fitness bracelets and medical instruments. The vulnerabilities, which were found in Bluetooth ...
Telecom

When WiFi was designed, it was intended for high-speed data communications. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) set the standards for communications—that's the 802.11 protocol, a familiar number ...
Oct 23, 2019
1
470
Computer Sciences

Heat causes errors in the qubits that are the building blocks of a quantum computer, so quantum systems are typically kept inside refrigerators that keep the temperature just above absolute zero (-459 degrees Fahrenheit).
Feb 21, 2023
0
634
Electronics & Semiconductors

Stanford engineers have taken a big step toward making it practical for electric cars to recharge as they speed along futuristic highways built to "refuel" vehicles wirelessly.
May 5, 2020
3
1100
Engineering

The next generation of phones and wireless devices will need new antennae to access higher and higher frequency ranges. One way to make antennae that work at tens of gigahertz—the frequencies needed for 5G and higher devices—is ...
Oct 26, 2022
1
333
Energy & Green Tech

The electricity that lights our homes and powers our appliances also creates small magnetic fields that are present all around us. Scientists have developed a new mechanism capable of harvesting this wasted magnetic field ...
Mar 31, 2020
0
302
Internet

Optics-based technologies such as optical fibers have strongly influenced the age of wired communication. Now they look set to revolutionize wireless communications as well and solve key issues with traditional radio-based ...
Jun 4, 2020
1
81
Wireless communication is the transfer of information over a distance without the use of electrical conductors or "wires". The distances involved may be short (a few meters as in television remote control) or long (thousands or millions of kilometers for radio communications). When the context is clear, the term is often shortened to "wireless". Wireless communication is generally considered to be a branch of telecommunications.
It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable two way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers and or garage doors, wireless computer mice, keyboards and headsets, satellite television and cordless telephones.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA