Keeping GPUs young
Graphics processing units (GPUs) are used for many computationally intensive tasks. Their aging process can be slowed by clever management, as TU Wien (Vienna) and University of California (Irvine) have now shown.
Graphics processing units are not only used for displaying graphics. Today, they are frequently used for particularly challenging calculations – for example in scientific research or even Bitcoin-mining.
However, their performance usually decreases over time. As the individual cores of the processing unit age, they do not work together perfectly any more. TU Wien and the University of California, Irvine have therefore developed an improved chip management method, which distributes the processing tasks in an efficient way. In more than 95 % of cases, this can slow down the aging process of GPUs.
Highly Parallel Computing
"The standard computers that we are using at home just have a few processor cores. A graphics processing unit on the other hand consists of a large number of cores—typically hundreds or thousands", says Professor Muhammad Shafique (Institute for Computer Engineering, TU Wien). Therefore, GPUs are extremely useful for parallel calculations, in which a task can be broken down into many smaller calculations that can be solved independently from each other, by different cores at the same time.

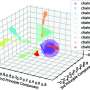
The cores, however, are never completely identical. "The structures on the GPU are very small. There will always be small imperfections and deviations due to the production process", says Muhammad Shafique. Therefore, aging has different effects on different cores. Under stress, the performance of different cores will drift apart.
This is a problem for parallel computing. When a task is distributed among many cores and the system has to wait for the last one to finish before the next step of the calculation can be started, the slowest core determines the overall speed of the process. This can drastically reduce the performance of the GPU.
Clever Management Techniques
Muhammad Shafique and the team of Professor Mohammad Al Faruque (University of California, Irvine) want to solve this problem using clever management methods: "First, it is crucial to know the status of the individual cores", says Muahmmad Shafique. "Then we can distribute different tasks in such a way among the cores that physical stress is optimally distributed."
Cores with similar properties are combined to "clusters", which are then assigned with more or less challenging tasks – depending on their current status. That way, the aging process can be slowed down, the overall performance of the system increases. "There have already been ideas on how to slow the aging process of GPUs with compiler-based techniques, but our method is much more effective. It works in more than 95 % of cases", says Muhammad Shafique.
More information: Haeseung Lee et al. Aging-aware Workload Management on Embedded GPU Under Process Variation, IEEE Transactions on Computers (2018). DOI: 10.1109/TC.2018.2789904