February 23, 2021 feature
A robot that allows users to virtually navigate remote environments
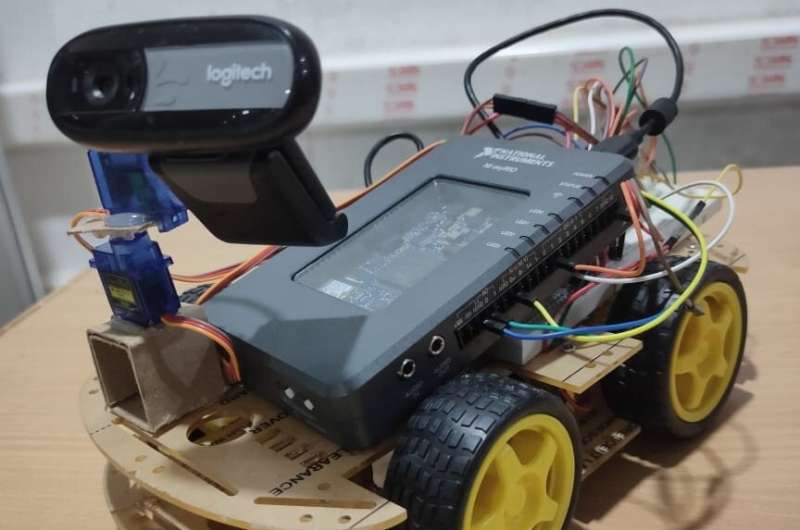

Two students who graduated from VR Siddartha Engineering College in Kanuru, India, have created a virtual telepresence robot that allows users to see what is happening in a remote location as if they were actually there. Their project, supervised by Professor V.N. Prudhvi Raj, provides a valuable example of how robots can be used to capture video data in real time and monitor places that are momentarily or permanently inaccessible to humans.
"I have recently graduated in electronics and instrumentation engineering from VR Siddhartha's Engineering College," Mani Babu Gorantla and Grandhi Sathya Venkata Krishna, the two researchers who created the robot, told TechXplore. "We developed this robot as our final project. It was inspired by an article about telepresence robots that we read in a magazine called Electronics For You."
The main objective of the recent study by Mani Babu, Krishna and Prudhvi was to allow users to see things that are happening in remote locations in real-time. To achieve this, they created a robot with an onboard camera and Wi-Fi capabilities, which captures videos and allows users to watch them instantly on their smartphone, on an internet browser or via virtual reality (VR) headsets.
"Whatever is captured by our robot's camera can be transmitted directly to a user's smartphone, which can also be placed in a VR box or headset, allowing users to view the environment in VR as if they were actually navigating it," Mani Babu and Krishna explained. "The user feels as if he/she is present at that location, as the robot's onboard camera moves in accordance with the user's head movements."
Initially, the researchers controlled the robot's movements and streamed the videos captured by its camera using an Arduino microcontroller and a Raspberry Pi, a minicomputer with no screen. They wanted to ensure that the robot's movements matched a user's head movements. To do this, they leveraged accelerometers and gyroscopes (i.e., sensors that can determine the position and orientation of an object), which are key components of most existing devices.

Essentially, the data collected by the accelerometers and gyroscopes in a user's smart phone is used to determine his/her head movements. This data is transferred to a Raspberry Pi device and then used to control the movements of the robot's camera, to ensure that they match a user's head movements.
"We used Arduino to move our robot back and forth, as well as right and left," Mani Babu and Krishna explained. "We decided to use two different controllers (Raspberry Pi and Arduino) because while Raspberry Pi can also control the robot's motor, it would have higher RAM; thus, we are giving it more time to process the video and stream it. This puts less burden on Raspberry Pi."
Although the first prototype of the robot was built using Raspberry Pi and Arduino, subsequently, the researchers substituted these two components with a more sophisticated device called MyRIO. MyRIO is a portable device that can serve both as a data processor and controller; thus, it can combine the capabilities of Raspberry Pi and Arduino devices.
"Initially, we used Raspberry Pi and Arduino to control the robot, but eventually, we decided to try using MyRIO instead, which is more expensive but has a higher processing capability; thus, it can simultaneously fulfill the tasks of Raspberry Pi and Arduino," Mani Babu and Krishna said. "Our robot could have many applications. In the context of our university, for example, it could be used by the principal or a head of department to monitor corridors."
While Mani Babu, Krishna and Prudhvi are not currently planning to commercialize the robot they created, their work could serve as an inspiration for other research teams, ultimately leading to the development of similar virtual telepresence robots. In the future, these robots could be used to monitor secluded or dangerous places from afar (e.g., looking for survivors during an earthquake or other natural disasters), to virtually view home or office environments when one is on holiday, and for a range of other applications.
More information: Implementation of virtual telepresence robot using two approaches Raspberry Pi and MyRIO. Advances in Systems Engineering(2021). DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-8025-3_52
© 2021 Science X Network