Putting the brakes on lithium-ion batteries to prevent fires
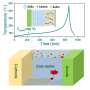
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are used to power everything from smart watches to electric vehicles, thanks to the large amounts of energy they can store in small spaces. When overheated, however, they're prone to catching fire or even exploding. But recent research published in Nano Letters offers a possible solution with a new technology that can swiftly put the brakes on a Li-ion battery, shutting it down when it gets too hot.
The chemistry found in many batteries is essentially the same: Electrons are shuttled through an electronic device in a circuit from one electrode in the battery to another. But in a Li-ion cell, the electrolyte liquid that separates these electrodes can evaporate when it overheats, causing a short circuit. In certain cases, short circuiting can lead to thermal runaway, a process in which a cell heats itself uncontrollably.
When multiple Li-ion cells are chained together—such as in electric vehicles—thermal runaway can spread from one unit to the next, resulting in a very large, hard-to-fight fire. To prevent this, some batteries now have fail-safe features, such as external vents, temperature sensors or flame-retardant electrolytes. But these measures often either kick in too late or harm performance. So, Yapei Wang, Kai Liu and colleagues wanted to create a Li-ion battery that could shut itself down quickly, but also work just as well as existing technologies.
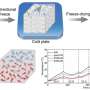
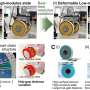
The researchers used a thermally-responsive shape memory polymer covered with a conductive copper spray to create a material that would transmit electrons most of the time, but switch to being an insulator when heated excessively. At around 197° F (91.6° C), a microscopic, 3D pattern programmed into the polymer appeared, breaking apart the copper layer and stopping the flow of electrons.
This permanently shut down the cell but prevented a potential fire. At this temperature, however, traditional cells kept running, putting them at risk of thermal runaway if they became hot again. Under regular operating temperatures, the battery with the new polymer maintained a high conductivity, low resistivity and similar cycling lifetime to a traditional battery cell. The researchers say that this technology could make Li-ion batteries safer without having to sacrifice their performance.
More information: Jichen Jia et al, Early Braking of Overwarmed Lithium-Ion Batteries by Shape-Memorized Current Collectors, Nano Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c03645