This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Without access to high-quality, reliable spatial data, government functions and services will suffer
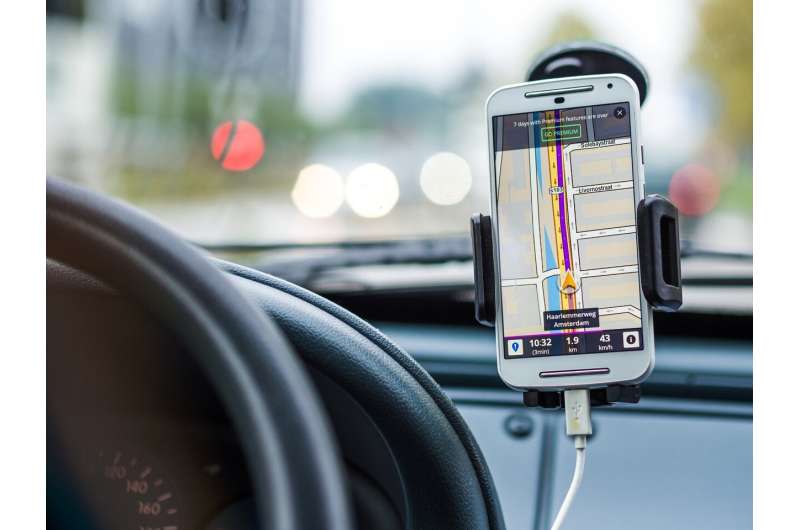

Within the rapidly changing landscape of data providers, governments must address concerns over who collects and uses data to support the public interest. Dr. Peter Johnson, a geographer at the University of Waterloo, is an expert on spatial data and navigating the complexities of this evolving landscape.
What's spatial data?
Every time you use a service like Google Maps or order anything online for delivery, accurate and up-to-date spatial data make those services work. Location data are collected from dozens of sources, including satellite imagery, official census programs, personal mobile devices, and traditional land surveys.
What's the state of spatial data control in Canada?
Canada's spatial data are created, owned, used, and shared between many organizations. Governments at all levels have long been the dominant collector and provider, however, this has changed as private companies, particularly technology companies, invest in mass data collection. As a result, there are now multiple sources of spatial data that vary considerably in their detail, purpose, and reliability.
How would inadequate spatial data control impact Canadians?
Tensions are emerging over who should be collecting data, how data are shared or licensed between users, and what this means for the ability of governments to have the spatial data necessary to support essential functions and services. Government functions and services will suffer without access to high-quality, reliable spatial data. In many areas around the world, insufficient spatial data prevents service provision like health care, emergency response, and free and fair elections. In addition, it can restrict the building of infrastructure and slow progress in addressing the impacts of climate change.
What must the government do to control spatial data use in the public interest?
There are many approaches that governments could take, such as investing in expanding their data collection abilities, contracting out or licensing data from private companies, or establishing a data trust where a neutral third-party acts as a broker between data collection companies and government agencies. Each approach has benefits and tradeoffs—these are the areas my research aims to investigate.