This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Green composite material made from flax and chitosan

Composite materials provide stability in aircraft parts, sports equipment, and everyday household items. However, most of these materials have a poor carbon footprint and are not naturally degradable. A more sustainable alternative has been developed by a team from the University of Stuttgart led by Dr. Linus Stegbauer from the Institute of Interfacial Process Engineering and Plasma Technology (IGVP). This completely bio-based composite material is made of flax fibers and the biopolymer chitosan. The study is published in the journal Composites Science and Technology.
As the name suggests, composites consist of at least two starting materials combined in such a way that the end product has certain properties (e.g., it is both light and strong). Many conventional composite materials contain fossil-based polymers. Recycling such composites is complicated and energy-intensive—if even possible at all—and degrades the properties of the material. That's why most composites end up in landfills or incineration plants after use, thereby causing additional CO2 emissions.
Renewable components
In order to be able to offer more environmentally friendly products, the composites industry needs alternatives to fossil materials. The challenge is to find the right balance between economical production, excellent material properties, and sustainability. Biocomposites made from natural components that are biodegradable, non-toxic, and renewable—and thus have a low carbon footprint—offer one possible solution.
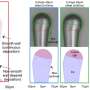
Such a material has now been developed by researchers from the Institute of Interfacial Process Engineering and Plasma Technology (IGVP), the Institute of Aircraft Engineering (IFB), and the Institute of Computer Architecture and Computer Engineering (ITI). The team has successfully produced chitosan–flax biocomposites. These materials consist of flax fibers, which act as a reinforcing element, and the biopolymer chitosan, which is derived from chitin and holds the flax fibers together.
"We have conducted extensive studies to test and optimize the manufacturing process in order to achieve mechanical properties in line with those of fossil-based composites," explains Dr. Linus Stegbauer, who initiated the research together with Dr. Stefan Carosella from the IFB.
Among other things, the researchers found that chitosan with a shorter polymer chain length is best suited for impregnating the flax fibers. This minimizes the porosity of the composites. The chitosan–flax composite is not only naturally degradable and made exclusively from CO2-neutral raw materials but also has greater stiffness in terms of density and thus greater lightweight construction potential than composites containing epoxy resin.
"This gives our bio-based material a competitive advantage. For example, when it comes to reducing fuel consumption in automotive construction," says Stegbauer. According to the study, the chitosan–flax composite could also replace conventional materials in construction, sports equipment, and cargo crates.
More information: Amrita Rath et al, Fabrication of chitosan-flax composites with differing molecular weights and its effect on mechanical properties, Composites Science and Technology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.109952