This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
New neural network uses common sense to make fake bird images from text
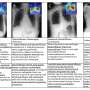
In an effort to generate high-quality images based on text descriptions, a group of researchers in China built a generative adversarial network that incorporates data representing common-sense knowledge. Their method uses common sense to clarify the starting point for image generation and also uses common sense to enhance different specific features of the generated image at three different levels of resolution. The network was trained using a database of bird images and text descriptions. The generated bird images achieved competitive scores when compared with those produced using other neural network methods.
The group's research was published in Intelligent Computing.
Given that "a picture is worth a thousand words," the shortcomings of the currently available text-to-image frameworks are hardly surprising. If you want to generate an image of a bird, the description you give to a computer might include its size, the color of it body and the shape its beak. To produce an image, the computer must still decide many details about how to display the bird, such as which way the bird is facing, what should be in the background and whether its beak is open or closed.
If the computer had what we think of as common-sense knowledge, it would make decisions about depicting unspecified details more successfully. For example, a bird might stand on one leg or two legs, but not three.
When quantitatively measured against its predecessors, the authors' image generation network achieved competitive scores using metrics that measure fidelity and distance from real images. Qualitatively, the authors characterize the generated images as generally consistent, natural, sharp and vivid.
"We firmly believe that the introduction of common sense can greatly promote the development of text-to-image synthesis," the research article concludes.
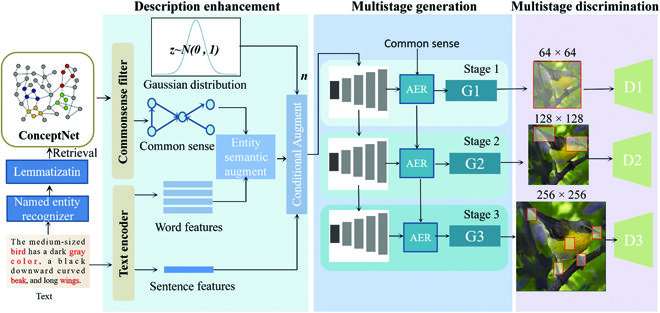
The authors' neural network for generating images from text consists of three modules. The first one enhances the text description that will be used to generate the image. ConceptNet, a data source that represents general knowledge for language processing as a graph of related nodes, was used to retrieve pieces of common-sense knowledge to be added to the text description.
The authors added a filter to reject useless knowledge and select the most relevant knowledge. To randomize the generated images, they added some statistical noise. The input to the image generator thus consists of the original text description, analyzed as a sentence and as separate words, plus selected bits of common-sense knowledge from ConceptNet, plus noise.
The second module generates images in multiple stages. Each stage corresponds to an image size, starting with a small image of 64 x 64 pixels and increasing to 128 x 128 and then 256 x 256. The module relies on the authors' "adaptive entity refinement" unit, which incorporates common-sense knowledge of the details needed for each size of image.
The third module examines generated images and rejects those that do not match the original description. The system is a "generative adversarial network" because it has this third part that checks the work of the generator. Since the authors' network is "common-sense driven," they call their network CD-GAN.
CD-GAN was trained using the Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 dataset, which catalogs 200 bird species using 11,788 specially annotated images.
More information: Guokai Zhang et al, CD-GAN: Commonsense-Driven Generative Adversarial Network with Hierarchical Refinement for Text-to-Image Synthesis, Intelligent Computing (2023). DOI: 10.34133/icomputing.0017