This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Vibrating vests translate music for deaf concertgoers
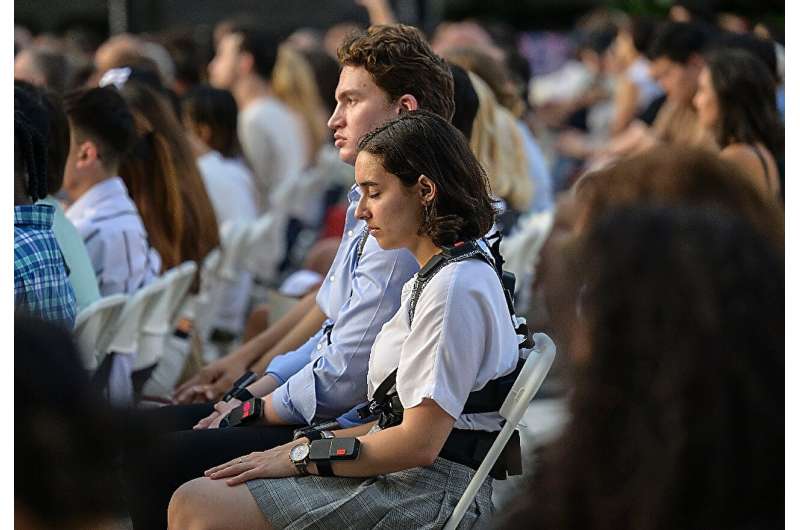

The violins reverberate in the ribcage, while cello and bass are felt a little further down, with horns in the shoulders and, more often than not, soloists in the wrists.
That's one way audio expert Patrick Hanlon programs haptic suits, designed to enable concertgoers who are deaf or hard of hearing to experience orchestral music, as initiatives to improve inclusivity at live music performances break new ground.
At a recent classical concert at Manhattan's Lincoln Center, audience members had the chance to try on the wireless vests, featuring 24 points of vibration translating the music onstage.
"It engages the body," Hanlon told AFP prior to the show, giving attendees a "3D-surround experience through vibrations."
Hanlon is a co-founder of Music: Not Impossible, an arm of Not Impossible Labs, which employs tech to try to alleviate social barriers, including those around disability.
Previous methods that deaf and hard of hearing individuals would use to enjoy live music included literally putting their hands on speakers, or holding a balloon to feel vibrations in their fingertips.
The aim of the vests—along with bands at the wrists or ankles—is to allow for a full-body experience, creating sensations that render the feelings music can evoke.
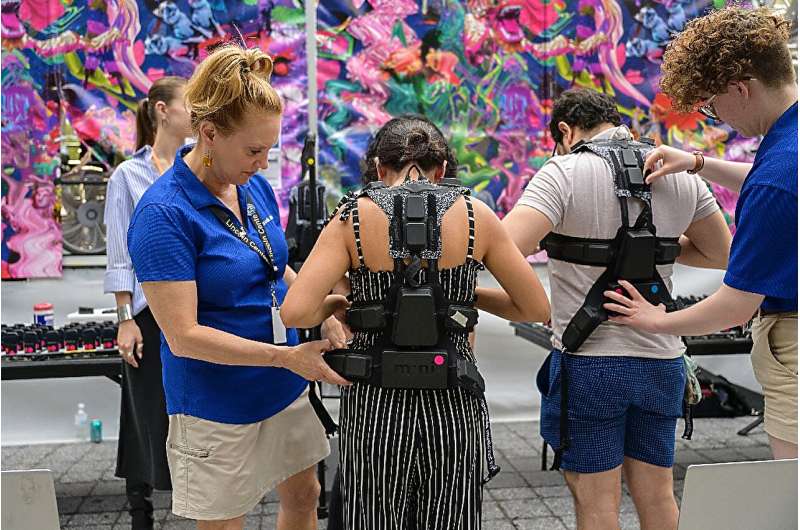

"Nobody expects it to be so engaging," Hanlon said of the vests. "And when you see it in people's eyes, it's magical."
Jay Zimmerman, a composer whose ability to hear was damaged due to the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, says the vests are an example of new technology offering more flexibility and dynamism than had been available previously.
"My hope is down the road, is that we will be able to let deaf kids have experiences with real vibrations and real materials up close, so they start building this library of auditory memory—even if it's not auditory through their ears, it's just different sensations," he told AFP.
"I think if we can put it all together, there's real opportunities for us."
'Immersion'
Lincoln Center, the prestigious arts complex on New York's Upper West Side, began working with Music: Not Impossible in 2021, both for orchestra shows and for their popular outdoor silent disco series.
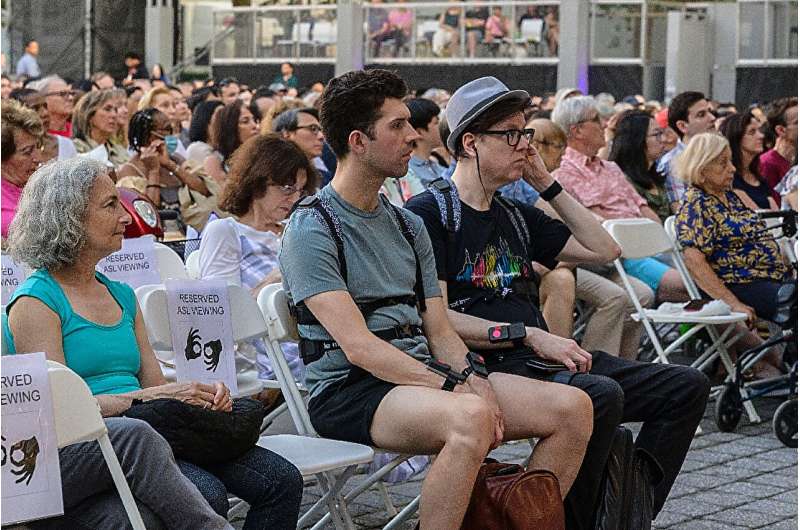
Its most recent collaboration had 75 vests on offer during its outdoor concert as part of Korean Arts Week, which featured renditions of Korean folk music as well as Mozart's Concerto No. 2.
Liza Fiol-Matta was among the attendees, and though she is not hard of hearing, she was excited to test the tech.
"Music is my major love, and the idea that there can be an experiential sense of the music for anybody" is exciting, she said. "But also for the deaf and hearing impaired—that's perfect."
"I love the idea of immersion, the whole immersive experience... music happens at so many different levels."
Flavia Naslausky, the business head for Music: Not Impossible, described how during early testing, Mandy Harvey—a singer who lost her hearing after an illness—was able to match the sound of the music after feeling the vibration that translated it.
-
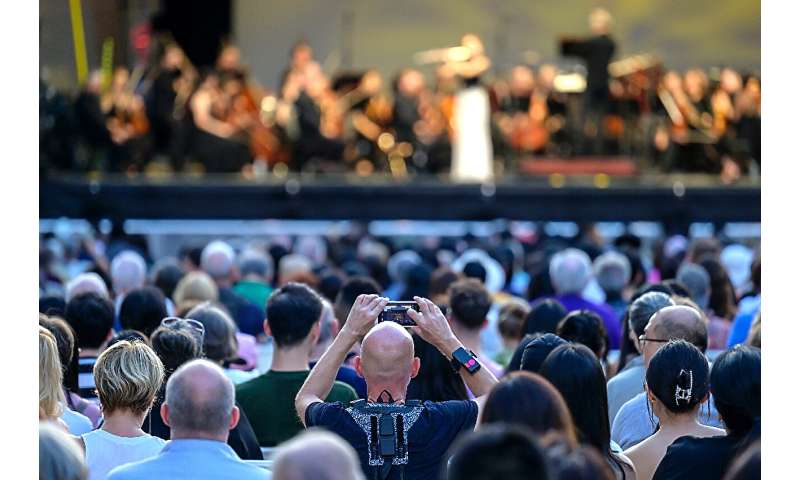

Haptic vests were recently used at a classical music concert at New York's Lincoln Center, but they can be adjusted to fit the vibe of any genre. -
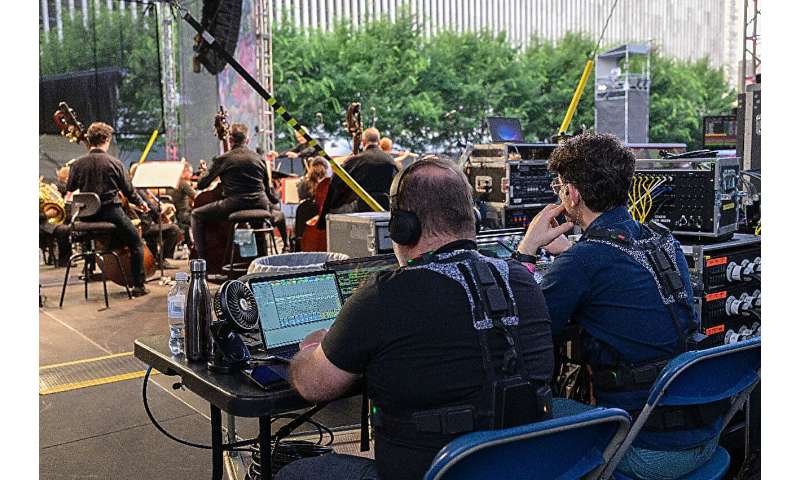

Technicians control haptic suits that deliver 24 points of vibration, translating the music played onstage to the wearer.
"That's when we knew that we were right on, because if somebody that wasn't hearing, from that vibration could match that note—we were on the right direction," Naslausky said.
Music: Not Impossible's vests are not genre-limited. Hanlon explained audio leads like him can adjust the vibration points to fit a show's vibe, from rock to disco.
The vests have been used at Greta Van Fleet and Lady Gaga concerts.
Zimmerman is excited about the technology's potential—but there's still a far way to go.
"Ultimately, the big goal for me is that I will be able to feel a soft violin and it will be so gorgeous to my body and my mind that I would cry," he said. "And I could feel that exact same note come through a trombone blast and it will be so hilarious I'm going to laugh."
"That is the big dream."
© 2023 AFP